Distinct binding conformations of epinephrine with α- and β-adrenergic receptors
- PMID: 39218975
- PMCID: PMC11447022
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-024-01296-x
Distinct binding conformations of epinephrine with α- and β-adrenergic receptors
Abstract
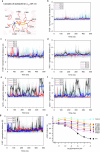
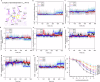
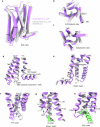
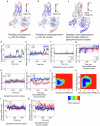
Agonists targeting α2-adrenergic receptors (ARs) are used to treat diverse conditions, including hypertension, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, pain, panic disorders, opioid and alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and cigarette cravings. These receptors transduce signals through heterotrimeric Gi proteins. Here, we elucidated cryo-EM structures that depict α2A-AR in complex with Gi proteins, along with the endogenous agonist epinephrine or the synthetic agonist dexmedetomidine. Molecular dynamics simulations and functional studies reinforce the results of the structural revelations. Our investigation revealed that epinephrine exhibits different conformations when engaging with α-ARs and β-ARs. Furthermore, α2A-AR and β1-AR (primarily coupled to Gs, with secondary associations to Gi) were compared and found to exhibit different interactions with Gi proteins. Notably, the stability of the epinephrine-α2A-AR-Gi complex is greater than that of the dexmedetomidine-α2A-AR-Gi complex. These findings substantiate and improve our knowledge on the intricate signaling mechanisms orchestrated by ARs and concurrently shed light on the regulation of α-ARs and β-ARs by epinephrine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- von Euler, U. S. Adrenergic neurotransmitter functions. Science173, 202–206, 10.1126/science.173.3993.202 (1971). - PubMed
-
- Philipp, M. & Hein, L. Adrenergic receptor knockout mice: distinct functions of 9 receptor subtypes. Pharm. Ther.101, 65–74, 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2003.10.004 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Brede, M., Philipp, M., Knaus, A., Muthig, V. & Hein, L. alpha2-adrenergic receptor subtypes—novel functions uncovered in gene-targeted mouse models. Biol. Cell96, 343–348, 10.1016/j.biolcel.2004.03.006 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Keating, G. M. Dexmedetomidine: a review of its use for sedation in the intensive care setting. Drugs75, 1119–1130, 10.1007/s40265-015-0419-5 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

