Stromal cells and epigenetics: emerging key players of chronic inflammatory skin diseases
- PMID: 39219048
- PMCID: PMC11608854
- DOI: 10.5483/BMBRep.2024-0039
Stromal cells and epigenetics: emerging key players of chronic inflammatory skin diseases
Abstract
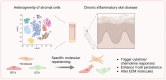
Epigenetic alterations play a crucial role in developmental processes, tissue regeneration, and cellular differentiation. Epigenetic changes are dynamically reversible. Various drugs that target DNA methyltransferases or histone deacetylases have demonstrated their ability to restore normal epigenetic patterns in a number of diseases. While the involvement of epigenetic modifications has been identified in chronic inflammatory diseases, their specific impact on skin inflammation in stromal cells remains unclear. This mini-review explores the role of stromal cells in chronic inflammatory skin diseases, focusing on epigenetic modifications of stromal cells such as fibroblasts, lymphatic, and blood vascular endothelial cells in both healthy and diseased skin. We also provide an overview of recent findings that highlight the contribution of stromal cells, including fibroblasts, to inflammatory and remodeling processes through epigenetic changes in the context of chronic inflammatory conditions. Investigating epigenetic reprogramming of stromal cells might lead to novel strategies for treating chronic inflammatory skin diseases. [BMB Reports 2024; 57(11): 465-471].
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicting interests.
Figures

References
-
- Novoseletskaya E, Grigorieva O, Nimiritsky P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-produced components of extracellular matrix potentiate multipotent stem cell response to differentiation stimuli. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:555378. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.555378.1a8f341987074ed687d93a8a2f955750 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

