De Novo Missense Variations of ATP8B2 Impair Its Phosphatidylcholine Flippase Activity
- PMID: 39219493
- PMCID: PMC11529410
- DOI: 10.1080/10985549.2024.2391829
De Novo Missense Variations of ATP8B2 Impair Its Phosphatidylcholine Flippase Activity
Abstract
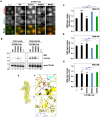
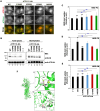
P4-ATPases comprise a family of lipid flippases that translocate lipids from the exoplasmic (or luminal) to the cytoplasmic leaflet of biological membranes. Of the 14 known human P4-ATPases, ATP8B2 is a phosphatidylcholine flippase at the plasma membrane, but its physiological function is not well understood. Although ATP8B2 could interact with both CDC50A and CDC50B, it required only the CDC50A interaction for its exit from the endoplasmic reticulum and subsequent transport to the plasma membrane. Three de novo monoallelic missense variations of ATP8B2 were found in patients with intellectual disability. None of these variations affected the interaction of ATP8B2 with CDC50A or its localization to the plasma membrane. However, variations of either of two amino acid residues, which are conserved in all P4-ATPases, significantly reduced the phosphatidylcholine flippase activity of ATP8B2. Furthermore, mutations in the corresponding residues of ATP8B1 and ATP11C were found to decrease their flippase activities toward phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine, respectively. These results indicate that the conserved amino acid residues are crucial for the enzymatic activities of the P4-ATPases.
Keywords: Lipid bilayer; P-type ATPase; flippase.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phospholipid flippase activities and substrate specificities of human type IV P-type ATPases localized to the plasma membrane.J Biol Chem. 2014 Nov 28;289(48):33543-56. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.593012. Epub 2014 Oct 14. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25315773 Free PMC article.
-
Substrates of P4-ATPases: beyond aminophospholipids (phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine).FASEB J. 2019 Mar;33(3):3087-3096. doi: 10.1096/fj.201801873R. Epub 2018 Dec 3. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30509129 Review.
-
Novel phosphatidylinositol flippases contribute to phosphoinositide homeostasis in the plasma membrane.Biochem J. 2024 Sep 18;481(18):1187-1202. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20240223. Biochem J. 2024. PMID: 39258799
-
The CDC50A extracellular domain is required for forming a functional complex with and chaperoning phospholipid flippases to the plasma membrane.J Biol Chem. 2018 Feb 9;293(6):2172-2182. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA117.000289. Epub 2017 Dec 24. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29276178 Free PMC article.
-
P4-ATPases: lipid flippases in cell membranes.Pflugers Arch. 2014 Jul;466(7):1227-40. doi: 10.1007/s00424-013-1363-4. Pflugers Arch. 2014. PMID: 24077738 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Substrates, regulation, cellular functions, and disease associations of P4-ATPases.Commun Biol. 2025 Jan 28;8(1):135. doi: 10.1038/s42003-025-07549-3. Commun Biol. 2025. PMID: 39875509 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
