In Vitro and in Silico Analysis of α -Amylase Inhibitory Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Adhatoda vasica Leaves
- PMID: 39219710
- PMCID: PMC11365037
- DOI: 10.1177/27536130241270621
In Vitro and in Silico Analysis of α -Amylase Inhibitory Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Adhatoda vasica Leaves
Abstract
Objective: Diabetic individuals have a higher probability of suffering from illness and death due to small blood vessel-related problems such as retinopathy, neuropathy, nephropathy, and stroke than other complications. There are many synthetic anti-diabetic agents available, but these can be expensive and have undesirable pathological effects. The enzyme α-amylase (hydrolase), catalyzes the hydrolysis of starch to maltose and glucose via the cleavage of α-1,4-glucosidic linkages. Diabetes mellitus patients may benefit from a therapeutic strategy that involves slowing the hydrolysis of starch by inhibiting the activity of α-amylase. Thus, looking for cost-effective, natural, and safe antidiabetic agents is essential. This study aims to screen phytoconstituents and evaluate the in-vitro and in-silico α-amylase inhibitory activity of the ethanolic extract of Adhatoda vasica leaves.
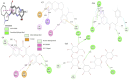
Methods: The extraction of Adhatoda vasica leaves was performed using ethanol via the Soxhlet extraction process. Different concentrations (100 μg/mL to 1000 μg/mL) of ethanolic extract, Acarbose, and Sitagliptin, were prepared and evaluated for α-amylase inhibitory activity using the spectrophotometric method. Molecular docking (AutodockVina 1.2.0) and toxicity profiling (SToPToX web server) studies were performed.
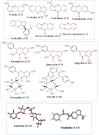
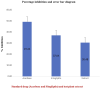
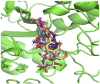
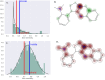
Results: The ethanolic extract of Adhatoda vasica leaves showed the highest percentage inhibition against α-amylase (56.763 ± 0.0035) at a concentration of 1000 μg/mL. The in-silico study supported this inhibitory activity. Vasicoline (C5) and Quercetin (C9), the active constitute of Adhatoda vasica, showed the best binding energies of -8.3 and -8.0 Kcal/mol, respectively against α-amylase enzyme (PDBID: 4W93). A toxicity study revealed the safety profile of the plant extract.
Conclusion: It was concluded that Adhatoda vasica leaves possess some bioactive compounds that are responsible for controlling blood glucose levels, and their identification, purification, and isolation may lead to the development of new therapeutic agents with fewer side effects than the available drugs.
Keywords: adhatoda vasica; anti-diabetic activity; molecular docking; α-amylase.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Valorization of Adhatoda vasica leaves: Extraction, in vitro analyses and in silico approaches.Front Nutr. 2023 Mar 17;10:1161471. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1161471. eCollection 2023. Front Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37063312 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative potential of Adhatoda vasica against anti-tubercular drugs induced hepatic impairments in female Wistar rats in relation to oxidative stress and xeno-metabolism.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113771. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113771. Epub 2020 Dec 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33388427
-
Inhibitory activity of Urena lobata leaf extract on alpha-amylase and alpha-glucosidase: in vitro and in silico approach.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 25;32(4):889-894. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2020-0430. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34214371
-
Exploring the pharmacological and chemical aspects of pyrrolo-quinazoline derivatives in Adhatoda vasica.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 8;10(4):e25727. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e25727. eCollection 2024 Feb 29. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38379997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Antidiabetic Activities of the Fruit of Parquetina nigrescens (Afzel.) Bullock and In Silico Identification of Its Antidiabetic Agent.Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024 Jan 26;18:11779322231223857. doi: 10.1177/11779322231223857. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Biol Insights. 2024. PMID: 38283284 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Optimization of the extraction methods and evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of Adhatoda Zeylanica extracts on artificially induced diabetic mice.Heliyon. 2025 Jan 2;11(1):e41627. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e41627. eCollection 2025 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2025. PMID: 39866458 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Padhi S, Nayak AK, Behera A. Type II diabetes mellitus: a review on recent drug based therapeutics. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;131(1):110708. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
