Metabolomics combined with intestinal microbiota reveals the mechanism of compound Qilian tablets against diabetic retinopathy
- PMID: 39220039
- PMCID: PMC11362098
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1453436
Metabolomics combined with intestinal microbiota reveals the mechanism of compound Qilian tablets against diabetic retinopathy
Abstract
Background: Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the common chronic complications of diabetes mellitus, which has developed into the leading cause of irreversible visual impairment in adults worldwide. Compound Qilian tablets (CQLT) is a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) developed for treating DR, but its mechanism is still unclear. This study explored the mechanism of action of CQLT in treating DR through metabolomics and intestinal microbiota.
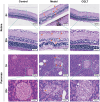
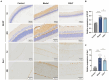
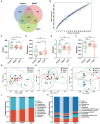
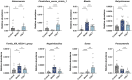
Methods: Histopathologic examination of the pancreas and retina of Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats and immunohistochemistry were used to determine the expression levels of retinal nerve damage indicators ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule-1 (Iba-1) and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP). Rat fecal samples were tested by LC-MS metabolomics to search for potential biomarkers and metabolic pathways for CQLT treatment of DR. Characteristic nucleic acid sequences of rat intestinal microbiota from each group were revealed using 16S rDNA technology to explore key microbes and related pathways for CQLT treatment of DR. At the same time, we investigated the effect of CQLT on the gluconeogenic pathway.
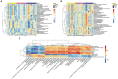
Results: After CQLT intervention, islet cell status was improved, Iba-1 and GFAP expression were significantly decreased, and abnormal retinal microvascular proliferation and exudation were ameliorated. Metabolomics results showed that CQLT reversed 20 differential metabolites that were abnormally altered in DR rats. Intestinal microbiota analysis showed that treatment with CQLT improved the abundance and diversity of intestinal flora. Functional annotation of metabolites and intestinal flora revealed that glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism, starch and sucrose metabolism were the main pathways for CQLT in treating DR. According to the results of correlation analysis, there were significant correlations between Iba-1, GFAP, and intestinal microbiota and metabolites affected by CQLT. In addition, we found that CQLT effectively inhibited the gluconeogenesis process in diabetic mice.
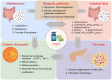
Conclusion: In conclusion, CQLT could potentially reshape intestinal microbiota composition and regulate metabolite profiles to protect retinal morphology and function, thereby ameliorating the progression of DR.
Keywords: compound Qilian tablets; diabetic retinopathy; intestinal microbiota; metabolic pathway; metabolomics.
Copyright © 2024 Jia, Liu, Wang, Ji, Wen, Xu and Ding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

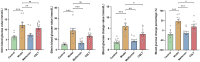
Similar articles
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking to Explore the Mechanism of Compound Qilian Tablets in Treating Diabetic Retinopathy.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025;21(3):333-347. doi: 10.2174/0115734099298932240308104437. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2025. PMID: 40420737 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Untargeted Metabolomics Reveal Potential Biomarkers of Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy in Asians.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 9;9:871291. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.871291. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35755823 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the mechanisms underlying the beneficial effect of Luo Tong formula on retinal function in diabetic rats via the "gut microbiota-inflammation-retina" axis.Chin Med. 2022 Dec 2;17(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s13020-022-00688-3. Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 36461068 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics of various samples advancing biomarker discovery and pathogenesis elucidation for diabetic retinopathy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Oct 27;13:1037164. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1037164. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36387907 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut microbiota and metabolites in diabetic retinopathy: Insights into pathogenesis for novel therapeutic strategies.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Aug;164:114994. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114994. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37301133 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of gut microbiota dysbiosis in the inflammatory pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy.Front Immunol. 2025 Jul 7;16:1604315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1604315. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40692792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bahr H. I., Abdelghany A. A., Galhom R. A., Barakat B. M., Arafa E. A., Fawzy M. S. (2019). Duloxetine protects against experimental diabetic retinopathy in mice through retinal GFAP downregulation and modulation of neurotrophic factors. Exp. Eye Res. 186:107742. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107742, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

