Diabetic mastopathy: about two cases
- PMID: 39220553
- PMCID: PMC11364885
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2024.48.28.42960
Diabetic mastopathy: about two cases
Abstract
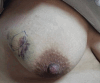
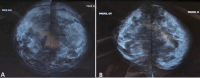
Diabetic mastopathy is a rare and benign pathology affecting young individuals with type 1 diabetes or autoimmune diseases. It clinically resembles breast cancer, necessitating a histological examination for a definitive diagnosis. These cases underscore the diagnostic challenges and the importance of histological examination. This report details two cases of diabetic mastopathy at Mohammed VI Hospital in Marrakech. The first case involved a 35-year-old with type 1 diabetes and mastodynia, revealing a 4 x 3 cm nodule in the left breast. Biopsies confirmed fibrous breast tissue with lymphocytic infiltrates, characteristic of diabetic mastopathy, with no recurrence during follow-up. The second case featured a 38-year-old with trisomy 21 and type 1 diabetes presenting with a right breast abscess. Drainage revealed lymphocytic infiltrates, confirming diabetic mastopathy. Though diagnostically challenging, diabetic mastopathy lacks a direct link to breast cancer. Long-term cancer risks in affected patients mirror the general population.
Keywords: Mastopathy; case report; diabetes; insulin.
Copyright: Karam Harou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Tomaszewski JE, Brooks JSJ, Hicks D, Livolsi VA. Diabetic mastopathy: A distinctive clinicopathologic entity. Hum Pathol. 1992 Jul;23(7):780–6. - PubMed
-
- Agochukwu NB, Wong L. Diabetic Mastopathy: A Systematic Review of Surgical Management of a Rare Breast Disease. Ann Plast Surg. 2017 Apr;78(4):471–475. - PubMed
-
- Chan CR, Ho RSL, Shek TWH, Kwong A. Diabetic Mastopathy. Breast J. 2013 Sep-Oct;19(5):533–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical