Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: a retrospective analysis of 36 cases
- PMID: 39220650
- PMCID: PMC11361986
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1416254
Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: a retrospective analysis of 36 cases
Abstract
Background and aims: Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa) is a rare type of mesenchymal neoplasm and lacks systematic reports. The aim was to analyze the features of hepatic PEComa in order to provide our own experience for diagnosis and management from a single center.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed clinical data, imaging findings, pathology, treatments and prognosis of 36 patients with hepatic PEComa in the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University from January 2016 to September 2023.
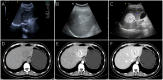
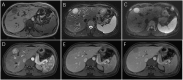
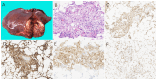
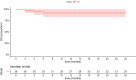
Results: 29 females and 7 males (median age, 47.8 years) were included in this study. The majority (26/36, 72.2%) of patients were diagnosed incidentally with non-specific symptoms. Abnormal enhancement of enlarged blood vessels (27/36,75%) can be observed on CT/MRI and only 7 patients (19.4%) were correctly diagnosed by imaging examinations. The positive immunohistochemical expressions were HMB-45(35/36,97.2%), Melan-A (34/35,97.1%), SMA (23/26,88.5%) and CD34(86.7%,26/30). Treatments include resection (24/36,67.7%), radiofrequency ablation (6/36,16.7%), transcatheter arterial chemoembolization(1/36,2.7%), conservative clinical follow-up(2/36,5.6%), and sirolimus-chemotherapy (3/36,8.3%). During the follow-up period (range, 2-81 months), except for one patient with a single intrahepatic recurrence and 3 malignant patients died in 6 months, the remaining patients had no signs of recurrence and metastasis.
Conclusions: Hepatic PEComa has no specific clinical features and mainly depends on clinicopathological characteristics for accurate diagnosis. Resection is the best treatment for benign PEComa, but TACE and radiofrequency ablation can also be considered in case of contraindications for surgery.
Keywords: PEComa; abdominal tumor; diagnosis; liver; treatment.
Copyright © 2024 Ji, Zhang, Liu, Zhang and Qiao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retrospective analysis of hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumour (PEComa) in a single centre for clinical diagnosis and treatment clinical diagnosis and treatment of hepatic PEComa.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Jun 24;101(25):e29506. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029506. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35758391 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor: Clinicopathological analysis of 26 cases with emphasis on disease management and prognosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Sep 21;27(35):5967-5977. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i35.5967. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34629813 Free PMC article.
-
Single-center Experience in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Hepatic Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Neoplasm.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022 Feb 28;10(1):72-79. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2020.00170. Epub 2021 Jun 21. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35233375 Free PMC article.
-
Bladder perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasm: Review on clinical features of this rare tumor.Urol Ann. 2024 Jan-Mar;16(1):28-35. doi: 10.4103/ua.ua_40_23. Epub 2024 Jan 25. Urol Ann. 2024. PMID: 38415228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic perivascular epithelioid cell tumor (PEComa): dynamic CT, MRI, ultrasonography, and pathologic features--analysis of 7 cases and review of the literature.Abdom Imaging. 2012 Oct;37(5):781-7. doi: 10.1007/s00261-012-9850-1. Abdom Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22278345 Review.
Cited by
-
Washout on Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound of Benign Focal Liver Lesions-A Review on Its Frequency and Possible Causes.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Apr 14;15(8):998. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15080998. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40310346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging features of primary liver perivascular epithelioid cell tumor with renal angiomyolipoma: a case report and literature review.Front Oncol. 2025 Jun 18;15:1534250. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1534250. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40606976 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and Treatment of Primary Hepatic Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor (PEComa) in Adults: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Jul 8;17(14):2276. doi: 10.3390/cancers17142276. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound of a Hepatic Perivascular Epithelioid Cell Tumor: A Case Report and Literature Review.Cureus. 2025 Apr 1;17(4):e81579. doi: 10.7759/cureus.81579. eCollection 2025 Apr. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40313453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fletcher C, Unni K, Mertens F. World health organization classification of tumours.Pathology and genetics of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC; (2002).
-
- Folpe AL, Mentzel T, Lehr HA, Fisher C, Balzer BL, Weiss SW. Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms of soft tissue and gynecologic origin: a clinicopathologic study of 26 cases and review of the literature. Am J Surg Pathol. (2005) 29(12):1558–75. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000173232.22117.37 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

