Association of smoking cessation with dynapenia among older lifetime smokers in Korea
- PMID: 39220716
- PMCID: PMC11365039
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/191822
Association of smoking cessation with dynapenia among older lifetime smokers in Korea
Abstract
Introduction: Muscle strength is known to play an important role in the health of older adults. The health burden of cigarette smoking among older adults remains significant. We investigated the association between smoking cessation and dynapenia among older lifetime smokers in Korea.
Methods: This study is a secondary dataset analysis of cross-sectional data from theKorea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) 2016- 2019. We included 1450 participants aged 65-79 years, excluding those who had never smoked. Dynapenia was defined as grip strength <28 kg for men and <18 kg for women based on the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia 2019 criteria. Multivariable logistic regression analysis evaluated the association between smoking cessation and dynapenia.
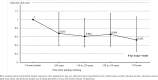
Results: Compared with current smokers, the adjusted odds ratio (AOR) of dynapenia in former smokers was 0.66 (95% CI: 0.44-0.99). The AORs for smoking cessation periods of ≤10 years, 10-20 years, 20-30 years, and >30 years were 0.67 (95% CI: 0.39-1.16), 0.61 (95% CI: 0.36-1.03), 0.65 (95% CI: 0.37-1.14), and 0.52 (95% CI: 0.25-1.06), respectively. The AOR for dynapenia significantly decreased with the years since smoking cessation (p for trend=0.043).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that smoking cessation can reduce the likelihood of dynapenia among older lifetime smokers, with a decreasing likelihood trend associated with longer cessation periods.
Keywords: Korea; dynapenia; older adults; smoking; smoking cessation.
© 2024 Yoo K. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have completed and submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The authors declare that they have no competing interests, financial or otherwise, related to the current work. Y.S. Park reports that since the initial planning of the work he has received support from the Hallym University Research Fund 2023 (grant number HURF-2023-25).
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
