Rapid detection of avian leukemia virus using CRISPR/Cas13a based lateral flow dipstick
- PMID: 39220765
- PMCID: PMC11362082
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1424238
Rapid detection of avian leukemia virus using CRISPR/Cas13a based lateral flow dipstick
Abstract
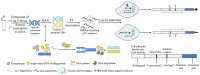
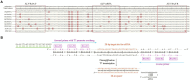
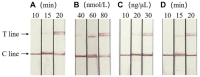
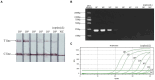
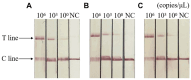
Avian leukemia virus (ALV) is one of the main pathogens of poultry tumor diseases, and has caused significant economic losses to the poultry industry since its discovery. Therefore, establishing a rapid detection method is essential to effectively prevent and control the spread of ALV. In this study, specific CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and recombinase-aided amplification (RAA) primers with T7 promoter were designed based on the relatively conserved sequence of avian leukemia virus. When crRNA recognized the target sequence, Cas13a protein was activated to cut the reporting probes, and then the detection results were read by using lateral flow dipstick (LFD). The RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD reaction system was constructed. The RAA amplification time, Cas13a protein concentration, crRNA concentration and CRISPR reaction time were optimized to evaluate the specificity, sensitivity and reproducibility of the system. Finally, RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD method was compared with Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-Agarose electrophoresis method and qPCR method in the detection of clinical samples, and the reliability of RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD method was evaluated. The results showed that the RAA-CRISPR/Cas13a-LFD method could effectively amplify the target gene at 37°C for 40 min, and the test results could be determined by LFD visual observation. The method had good specificity and no cross-reaction with Marek's disease virus (MDV), Fowl adenovirus (FAdV), Infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV), Newcastle disease virus (NDV), Infectious laryngotracheitis virus (ILTV), and Infectious bronchitis virus (IBV). The minimum detection limit of the method was 100 copies/μL, and it had good repeatability and stability. The coincidence rate of clinical detection reached 97.69% and 99.23%. In summary, this study established a simple, efficient, accurate and visualized ALV detection method, which can be used for the prevention and rapid clinical diagnosis of avian leukosis (AL).
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas13a; avian leukemia virus; lateral flow dipstick; rapid detection; recombinase-aided amplification.
Copyright © 2024 Li, Zhang, Zhang, Chen, Wang, Zhai and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

