Bioinformatics analysis of BTK expression in lung adenocarcinoma: implications for immune infiltration, prognostic biomarkers, and therapeutic targeting
- PMID: 39220827
- PMCID: PMC11358563
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-024-04053-z
Bioinformatics analysis of BTK expression in lung adenocarcinoma: implications for immune infiltration, prognostic biomarkers, and therapeutic targeting
Abstract
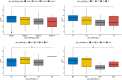
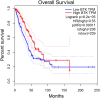
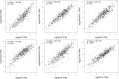
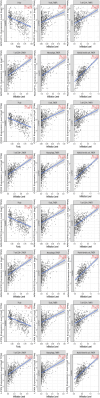
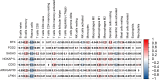
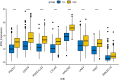
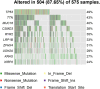
In recent years, as more and more lung-cancer patients have been treated with immunotherapeutic agents, their survival has been prolonged compared to before. It is well known that BTK (Bruton's tyrosine kinase) is predominantly found in cells of the hematopoietic system. However, there is a distinct lack of literature on BTK expression in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patients and its effect on the immune microenvironment. Consequently, the main goal of this investigation was to analyze how BTK expression in lung adenocarcinoma affects its progression, along with its prognostic significance, through the utilization of bioinformatics online resources and publicly available databases. Data on the sequencing results and clinical records of lung adenocarcinoma patients were gathered from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Based on the expression level of BKT, TCGA categorized lung adenocarcinoma patients into BTK high-expression and low-expression groups. We investigated the effects of BKT on clinicopathologic, genomic, and immunologic characteristics of lung adenocarcinoma patients. We analyzed BTK mRNA expression in tumors and normal tissues using two key resources: Tumor Immuno Estimation Resource 2.0 (TIMER 2.0) and Gene Expression Profiling Interactive Analysis 2 (GEPIA 2). We analyzed the prognosis of the patients using GEPIA2 and validated the results using univariate and multivariate analyses. In addition, we assessed BTK protein expression by Human Protein Atlas (HPA). We sought to elucidate the clinical prognostic significance of BTK in The TCGA using the online tool GEPIA 2. Furthermore, to clarify the biologic roles and pathways linked to BTK, we conducted a genomic enrichment analysis of the information. To predict the proportion of various immune cell infiltrations in the immune microenvironment of lung adenocarcinoma patients diagnosed in the TCGA database, we performed an analysis using the TIMER online tool. Using TIMER and CIBERSORT, the correlation between genes co-expressed with BTK and the corresponding tumor-infiltrating immune cells was explored; finally, the relationship between BTK expression and immune infiltration and immune checkpoints in the TMB group and the high and low groups was analyzed by R language analysis using the TCGA database. The expression of BTK provides some hints about the prognosis of the patients. The high expression of BTK is involved in immune response regulation signaling pathways, leukocyte-mediated immunity, leukocyte intercellular adhesion, graft rejection, and complement. Analysis of the GEPIA 2 database showed that BTK was co-expressed with the genes FGD2, SASH3, NCKAP1L, CD53, ARHGAP30 and LPXN. Increased expression of the above-mentioned genes resulted in increased proportions of CD8 + T cells, memory CD4 + T cells, B cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and decreased proportions of Treg cells and TH2 cells. In addition, our study revealed a strong positive correlation between various key immune checkpoints (e.g., PDCD1, CD274, PDCD1LG2, CTLA4, HAVCR2, LAG3, TIGIT, and SIGLEC15) and BTK expression. In conclusion, increased BTK expression in lung adenocarcinoma is closely associated with prolonged survival of lung-cancer patients. Moreover, the genes classified under the BTK high-expression group exhibit significant enrichment in immune-related pathways, suggesting a potential impact on the tumor microenvironment. We investigated the potential of BTK as a tumor suppressor gene in predicting prolonged patient survival. In addition, we further investigated the possibility that BTK further affects the immunotherapeutic response of patients by influencing the microenvironment of tumor immune infiltration, but the relevant mechanisms remain to be further studied.
Keywords: BTK expression; Bioinformatics; Immune microenvironment; Immunotherapy; Lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD); Prognostic marker.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2024. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

