The Differences in Parameters in Ultrasound Imaging and Biomechanical Properties of the Quadriceps Femoris with Unilateral Knee Osteoarthritis in the Elderly: A Preliminary Observational Study
- PMID: 39220855
- PMCID: PMC11363936
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S442610
The Differences in Parameters in Ultrasound Imaging and Biomechanical Properties of the Quadriceps Femoris with Unilateral Knee Osteoarthritis in the Elderly: A Preliminary Observational Study
Abstract
Purpose: Our study aims to evaluate differences in muscle parameters of the quadriceps muscles in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA) in older adults.
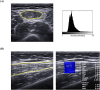
Methods: The study included 40 patients diagnosed with unilateral knee osteoarthritis in the KOA group (KG) and 40 asymptomatic elderly individuals in the control group (CG). Muscle ultrasonic mean echo intensity and shear modulus, as well as tone and stiffness of the rectus femoris (RF), vastus medialis (VM), and vastus lateralis (VL) were analyzed. Additionally, clinical correlations were performed.
Results: In the KG group, there were significant differences in echo intensity, shear modulus, and tone between the affected and unaffected sides for RF (p=0.003, 0.019, 0.014), while VM showed significant differences in shear modulus and tone (p=0.006, 0.002). Additionally, VL exhibited significant differences in echo intensity, shear modulus, and stiffness (p=0.007, 0.006, 0.010). Compared to the CG group, the KG group showed significant differences in echo intensity of the affected side RF (p=0.001). VM exhibited statistically significant differences in echo intensity and shear modulus (p < 0.001, p=0.008), while VL showed statistically significant differences in echo intensity, tone, and stiffness (p < 0.001, p=0.028, p < 0.001). The correlation results showed that patients with unilateral KOA, VM, and VL echo intensity were correlated with K-L grade (r = 0.443, p=0.004; r = 0.469, p=0.002). The tone of VL was correlated with VAS and WOMAC (r = 0.327, p=0.039; r = 0.344, p=0.030).
Conclusion: The parameters of the quadriceps femoris muscle exhibit asymmetry between the affected and unaffected sides in patients with unilateral KOA, as well as a difference between the dominant side of healthy older individuals and the affected side of KOA.
Keywords: knee osteoarthritis; muscle tone; quadriceps femoris; stiffness; ultrasound.
© 2024 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
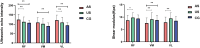
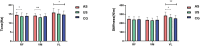
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

