Engineered nanoparticles for precise targeted drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer immunotherapy
- PMID: 39220871
- PMCID: PMC11365410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.010
Engineered nanoparticles for precise targeted drug delivery and enhanced therapeutic efficacy in cancer immunotherapy
Abstract
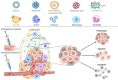
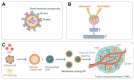
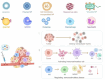
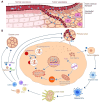
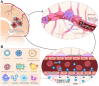
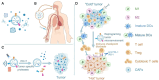
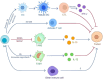
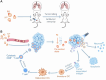
The advent of cancer immunotherapy has imparted a transformative impact on cancer treatment paradigms by harnessing the power of the immune system. However, the challenge of practical and precise targeting of malignant cells persists. To address this, engineered nanoparticles (NPs) have emerged as a promising solution for enhancing targeted drug delivery in immunotherapeutic interventions, owing to their small size, low immunogenicity, and ease of surface modification. This comprehensive review delves into contemporary research at the nexus of NP engineering and immunotherapy, encompassing an extensive spectrum of NP morphologies and strategies tailored toward optimizing tumor targeting and augmenting therapeutic effectiveness. Moreover, it underscores the mechanisms that NPs leverage to bypass the numerous obstacles encountered in immunotherapeutic regimens and probes into the combined potential of NPs when co-administered with both established and novel immunotherapeutic modalities. Finally, the review evaluates the existing limitations of NPs as drug delivery platforms in immunotherapy, which could shape the path for future advancements in this promising field.
Keywords: Blood–brain barrier; Cancer; Cancer immunotherapy; Drug delivery; Engineered nanoparticles; Nanomaterial; Nanomedicine; Tumor-barrier.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- de Visser K.E., Joyce J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: from cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell. 2023;41:374–403. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

