Semi-synthetic chondroitin sulfate CS-semi5 upregulates miR-122-5p, conferring a therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis via the p38/MMP13 pathway
- PMID: 39220883
- PMCID: PMC11365380
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.05.016
Semi-synthetic chondroitin sulfate CS-semi5 upregulates miR-122-5p, conferring a therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis via the p38/MMP13 pathway
Abstract
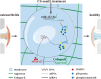
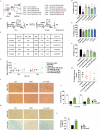
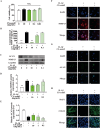
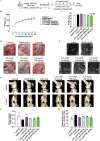
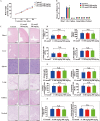
Osteoarthritis (OA) is an aging-associated disease characterized by joint stiffness pain and destroyed articular cartilage. Traditional treatments for OA are limited to alleviating various OA symptoms. There is a lack of drugs available in clinical practice that can truly repair cartilage damage. Here, we developed the chondroitin sulfate analog CS-semi5, semi-synthesized from chondroitin sulfate A. In vivo, CS-semi5 alleviated inflammation, provided analgesic effects, and protected cartilage in the modified Hulth OA rat model and papain-induced OA rat model. A bioinformatics analysis was performed on samples from OA patients and an exosome analysis on papain-induced OA rats, revealing miR-122-5p as the key regulator associated with CS-semi5 in OA treatment. Binding prediction revealed that miR-122-5p acted on the 3'-untranslated region of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, which was related to MMP13 regulation. Subsequent in vitro experiments revealed that CS-semi5 effectively reduced cartilage degeneration and maintained matrix homeostasis by inhibiting matrix breakdown through the miR-122-5p/p38/MMP13 axis, which was further validated in the articular cartilage of OA rats. This is the first study to investigate the semi-synthesized chondroitin sulfate CS-semi5, revealing its cartilage-protecting, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic properties that show promising therapeutic effects in OA via the miR-122-5p/p38/MMP13 pathway.
Keywords: Cartilage; Chondroitin sulfate; Extracellular matrix; Inflammation; MMP13; Osteoarthritis; miRNA; p38.
© 2024 The Authors.
Figures



References
-
- Bishnoi M., Jain A., Hurkat P., Jain S.K. Chondroitin sulphate: a focus on osteoarthritis. Glycoconj J. 2016;33:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Wang K., Qi L., Zhao L., Liu J., Guo Y., Zhang C. Degradation of chondroitin sulfate: mechanism of degradation, influence factors, structure–bioactivity relationship and application. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;301 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

