Innovative treatments for obesity and NAFLD: A bibliometric study on antioxidants, herbs, phytochemicals, and natural compounds
- PMID: 39220898
- PMCID: PMC11365328
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35498
Innovative treatments for obesity and NAFLD: A bibliometric study on antioxidants, herbs, phytochemicals, and natural compounds
Abstract
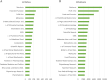
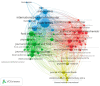
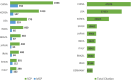
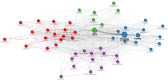
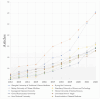
The increasing scientific interest in antioxidants and naturally derived compounds as potential remedies for obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has led to extensive research. The objective of this bibliometric analysis is to present an updated perspective on the topic of antioxidants, herbs, phytochemicals, and natural compounds, in the control of obesity and NAFLD, to identify new areas for future research. Publications from the years 2012-2022 were retrieved using the Scopus database. The research trends were analyzed using the Biblioshiny and VOSviewer tools. The field has seen a significant increase in research activity, as indicated by an annual growth rate of 10 % in the number of published manuscripts. China, Korea, and the USA emerged as the most prominent contributors in this specific field, supported by their notable volumes of publications and citations. The density analysis revealed that the most frequently occurring authors' keywords related to herbal species are, in rank order, Camelia sinensis, Momordica charantia, Curcuma longa, Ilex paraguariensis, Panax ginseng, Moringa oleifera, Garcinia cambogia, Garcinia mangostana, Zingiber officinale, and Cinnamomum verum. In the group of antioxidants, phytochemicals, and natural compounds, the top 10 were resveratrol, curcumin, quercetin, vitamin E, alpha-lipoic acid, vitamin C, chlorogenic acid, lycopene, fucoxanthin, and berberine. The co-occurrence analysis unveiled significant themes and potential trends, including a notable interest in the impact of herbal species, antioxidants, phytochemicals, and natural compounds on obesity and NAFLD through the modulation of the gut microbiome. Another recurring theme that arises, is the ongoing investigation of molecular targets that demonstrate anti-adipogenesis properties. The analysis presented in this study provides valuable insights for researchers investigating the efficacy of antioxidants, herbs, phytochemicals, and natural compounds in addressing obesity and NAFLD. Through the use of bibliometric methods, the study offers a comprehensive overview. Furthermore, the findings of this analysis can serve as a foundation for future research in this specific domain.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Biblioshiny; Herbs; NAFLD; Natural compounds; Obesity; Phytochemicals; Scopus; VOSviewer.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Lin X., Li H. Obesity: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021;12 https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fendo.2021.706978 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

