Yishen Huazhuo decoction regulates microglial polarization to reduce Alzheimer's disease-related neuroinflammation through TREM2
- PMID: 39220981
- PMCID: PMC11363852
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35800
Yishen Huazhuo decoction regulates microglial polarization to reduce Alzheimer's disease-related neuroinflammation through TREM2
Abstract
Background: Aging is the primary risk factor for the onset of Alzheimer's disease (AD). Inflamma-aging is a major feature in the process of aging, and the chronic neuroinflammation caused by inflamma-aging is closely related to AD. As the main participant of neuroinflammation, the polarization of microglia (MG) could influence the development of neuroinflammation.
Objective: This study aims to observe the impact of YHD on microglia (MG) polarization and neuroinflammation to delay the onset and progression of AD.
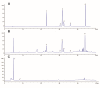
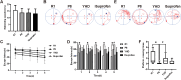
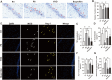
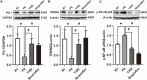
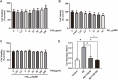
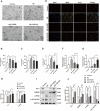
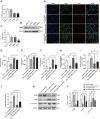
Methods: In vivo experiment, four-month senescence accelerated mouse prone 8 (SAMP8) were used as the model group, the SAMR1 mice of the same age were used as the control group. In YHD group, 6.24 g/kg YHD was intragastrically administrated continuously for 12 weeks, and Ibuprofen 0.026 g/kg in positive control group. Morris Water Maze test was used to evaluate the learning and memory ability, Nissl's staining and immunofluorescence double staining for neuron damage and MG M1/M2 polarization, Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) for neuroinflammation biomarkers in hippocampus, Western blot for key protein expression of TREM2/NF-κB signaling pathway. In vitro experiments, 10 μM/l Aβ1-42 induced BV-2 cell model was used to re-verify the effect of YHD regulating MG polarization to reduce neuroinflammation. Also, TREM2 small interfering RNA (siRNA) was used to clarify the key target of YHD.
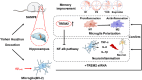
Results: YHD could improve the learning and memory ability of SAMP8 mice evaluated by the Morris Water Maze test. Like Ibuprofen, YHD could regulate the M1/M2 polarization of MG and the levels of neuroinflammatory markers TNF-α and IL-10 in hippocampus, and relieve neuroinflammation and neuron loss. In addition, YHD could also regulate the expression of PU.1, TREM2, p-NF-κB P65 in the TREM2/NF-κB signaling pathway. Further in vitro experiments, we found that YHD had a significant regulatory effect on Aβ1-42-induced BV-2 cell polarization, and it could significantly increase PU.1, TREM2, decrease p-NF-κB P65, p-IKKβ, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β. At the same time, using siRNA to inhibit TREM2, it proved that TREM2 was a key target for YHD to promote Aβ1-42-induced BV-2 cell M2 polarization to reduce neuroinflammation.
Conclusions: YHD could regulate the TREM2/NF-κB signaling pathway through TREM2, thereby to adjust MG polarization and reduce AD-related neuroinflammation.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Microglial polarization; Neuroinflammation; TREM2; Yishen Huazhuo decoction (YHD).
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yishen Huazhuo Decoction Induces Autophagy to Promote the Clearance of Aβ1-42 in SAMP8 Mice: Mechanism Research of a Traditional Chinese Formula Against Alzheimer's Disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2020;19(4):276-289. doi: 10.2174/1871527319666200604174223. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32496993
-
Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Inhibits Aβ1-42-Induced Neuroinflammation by Modulating the Phenotypic Transformation of Microglia via TREM2/TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in BV-2 Cells.Neurochem Res. 2022 Mar;47(3):748-761. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03484-x. Epub 2021 Nov 16. Neurochem Res. 2022. PMID: 34783973
-
[Xixin Decoction improves learning and memory ability of SAMP8 by enhancing neuroprotective effect and inhibiting neuroinflammation].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Sep;48(18):5032-5040. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230419.406. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802845 Chinese.
-
Downregulation of Nogo-B ameliorates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through regulating microglia polarization via TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway.Neurochem Int. 2023 Jul;167:105553. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2023.105553. Epub 2023 May 23. Neurochem Int. 2023. PMID: 37230196 Review.
-
The potential and challenges of TREM2-targeted therapy in Alzheimer's disease: insights from the INVOKE-2 study.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Apr 25;17:1576020. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1576020. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40353063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Modulating Neuroinflammation as a Prospective Therapeutic Target in Alzheimer's Disease.Cells. 2025 Jan 22;14(3):168. doi: 10.3390/cells14030168. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis and therapeutic applications of microglia receptors in Alzheimer's disease.Front Immunol. 2025 Feb 14;16:1508023. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1508023. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40028337 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hane F.T., Lee B.Y., Leonenko Z. Recent progress in Alzheimer's disease research, Part 1: pathology. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;57(1):1–28. - PubMed
-
- Corpas R., Hernandez-Pinto A.M., Porquet D., Hernandez-Sanchez C., Bosch F., Ortega-Aznar A., et al. Proinsulin protects against age-related cognitive loss through anti-inflammatory convergent pathways. Neuropharmacology. 2017;123:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Calsolaro V., Edison P. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease: current evidence and future directions. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12(6):719–732. - PubMed
-
- Bradburn S., Murgatroyd C., Ray N. Neuroinflammation in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019;50:1–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

