HPLC-DAD method for simultaneous determination of gallic acid, catechins, and methylxanthines and its application in quantitative analysis and origin identification of green tea
- PMID: 39220986
- PMCID: PMC11365376
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35819
HPLC-DAD method for simultaneous determination of gallic acid, catechins, and methylxanthines and its application in quantitative analysis and origin identification of green tea
Abstract
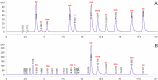
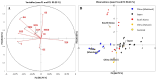
The high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a diode array detector (HPLC-DAD) was optimized for the simultaneous determination of 11 compounds, belonging to polyphenols (gallic acid and seven catechins) and methylxanthines (caffeine, theobromine, and theophylline). The results obtained for all the validation parameters of the HPLC-DAD method showed that the method is sensitive enough for routine analysis with basic chromatographic equipment, thus it has a significant potential to be highly applicable in common laboratory practice. The method was used in the analysis of 60 green tea infusions originating from four tea-producing countries. The dataset contributes to enhancing current data on green tea. The analysis of green tea extracts revealed significant differences depending on the origin of the samples. Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) was applied to test the accuracy of identification of the origin of the tea samples, based on the chemical composition of tea with a focus on polyphenolic compounds and methylxanthines analysed in this study. Based on cross-validation results, the model showed 93.75 % accuracy in the classification of green tea originating from Japan, China (Mainland), China (Taiwan) and South Korea.
Keywords: Green tea; HPLC-DAD; Method validation; Methylxanthines; Polyphenols.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Chemometrics-enhanced high performance liquid chromatography-diode array detection strategy for simultaneous determination of eight co-eluted compounds in ten kinds of Chinese teas using second-order calibration method based on alternating trilinear decomposition algorithm.J Chromatogr A. 2014 Oct 17;1364:151-62. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2014.08.068. Epub 2014 Aug 27. J Chromatogr A. 2014. PMID: 25223614
-
Multivariate analysis of the composition of bioactive in tea of the species Camellia sinensis.Food Chem. 2019 Feb 1;273:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.030. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30292372
-
Analytical validation and greenness assessment of HPLC-DAD method for methylxanthines analysis.Acta Chim Slov. 2025 Mar 3;72(1):180-194. doi: 10.17344/acsi.2024.8971. Acta Chim Slov. 2025. PMID: 40109056
-
Study of catechin and xanthine tea profiles as geographical tracers.J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Mar 27;50(7):1833-9. doi: 10.1021/jf0114435. J Agric Food Chem. 2002. PMID: 11902920
-
Comparison of the chemical constituents of aged pu-erh tea, ripened pu-erh tea, and other teas using HPLC-DAD-ESI-MSn.J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Aug 24;59(16):8754-60. doi: 10.1021/jf2015733. Epub 2011 Aug 3. J Agric Food Chem. 2011. PMID: 21793506
Cited by
-
Unveiling Synergistic Antioxidant Effects of Green Tea and Peppermint: Role of Polyphenol Interactions and Blend Preparation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 28;26(13):6257. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136257. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40650033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mamati G.E., Liang Y., Lu J. Expression of basic genes involved in tea polyphenol synthesis in relation to accumulation of catechins and total tea polyphenols. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006;86:459–464. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.2368. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

