Anticoagulation in device-detected atrial fibrillation with or without vascular disease: a combined analysis of the NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESiA trials
- PMID: 39222018
- PMCID: PMC11631065
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae596
Anticoagulation in device-detected atrial fibrillation with or without vascular disease: a combined analysis of the NOAH-AFNET 6 and ARTESiA trials
Abstract
Background and aims: The optimal antithrombotic therapy in patients with device-detected atrial fibrillation (DDAF) is unknown. Concomitant vascular disease can modify the benefits and risks of anticoagulation.
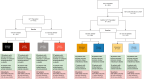
Methods: These pre-specified analyses of the NOAH-AFNET 6 (n = 2534 patients) and ARTESiA (n = 4012 patients) trials compared anticoagulation with no anticoagulation in patients with DDAF with or without vascular disease, defined as prior stroke/transient ischaemic attack, coronary or peripheral artery disease. Efficacy outcomes were the primary outcomes of both trials, a composite of stroke, systemic arterial embolism (SE), myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism or cardiovascular death, and stroke or SE. Safety outcomes were major bleeding or major bleeding and death.
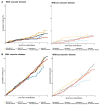
Results: In patients with vascular disease (NOAH-AFNET 6, 56%; ARTESiA, 46%), stroke, myocardial infarction, systemic or pulmonary embolism, or cardiovascular death occurred at 3.9%/patient-year with and 5.0%/patient-year without anticoagulation (NOAH-AFNET 6), and 3.2%/patient-year with and 4.4%/patient-year without anticoagulation (ARTESiA). Without vascular disease, outcomes were equal with and without anticoagulation (NOAH-AFNET 6, 2.7%/patient-year; ARTESiA, 2.3%/patient-year in both randomized groups). Meta-analysis found consistent results across both trials (I2heterogeneity = 6%) with a trend for interaction with randomized therapy (pinteraction = .08). Stroke/SE behaved similarly. Anticoagulation equally increased major bleeding in vascular disease patients [edoxaban, 2.1%/patient-year; no anticoagulation, 1.3%/patient-year; apixaban, 1.7%/patient-years; no anticoagulation, 1.1%/patient-year; incidence rate ratio 1.55 (1.10-2.20)] and without vascular disease [edoxaban, 2.2%/patient-year; no anticoagulation, 0.6%/patient-year; apixaban, 1.4%/patient-year; no anticoagulation, 1.1%/patient-year; incidence rate ratio 1.93 (0.72-5.20)].
Conclusions: Patients with DDAF and vascular disease are at higher risk of stroke and cardiovascular events and may derive a greater benefit from anticoagulation than patients with DDAF without vascular disease.
Keywords: Atrial fibrillation; Device-detected atrial fibrillation; Oral anticoagulation; Stroke; Trial.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures




References
-
- Ruff CT, Giugliano RP, Braunwald E, Hoffman EB, Deenadayalu N, Ezekowitz MD, et al. Comparison of the efficacy and safety of new oral anticoagulants with warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation: a meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet 2014;383:955–62. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62343-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BMBF
- German Ministry of Education and Research, Berlin, Germany
- FKZ 81X2800182/German Centre for Cardiovascular Research, Berlin, Germany
- Daiichi Sankyo Europe
- 633196/European Union CATCH ME
- 847770/AFFECT EU
- 965286/MAESTRIA
- AA/18/2/34218/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- Ki 509167694/German Research Foundation
- Leducq Foundation
- 01-002-2022-0118/Dutch Heart Foundation
- 201610PTJ-378238/Canadian Institutes of HealthResearch
- Bristol Myers Squibb-Pfizer Alliance
- Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada
- Canadian Stroke Prevention Intervention Network
- Hamilton Health Sciences
- Accelerating Clinical Trials Network
- Population Health Research Institute
- Medtronic
- 648131/Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 847770/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme
- 101095480/European Union's Horizon Europe research and innovation programme
- German Centre for Cardiovascular Research
- BMBF 01ZX1408A/German Ministry of Research and Education
- 031L0239/ERACoSysMed3
- Wolfgang Seefried project funding German Heart Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

