Exploring the Potential of Ellagic Acid in Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention: Recent Advances and Future Directions
- PMID: 39222186
- PMCID: PMC11574235
- DOI: 10.1007/s40487-024-00296-1
Exploring the Potential of Ellagic Acid in Gastrointestinal Cancer Prevention: Recent Advances and Future Directions
Abstract
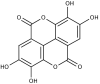
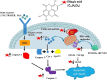
Gastrointestinal (GI) cancers are a significant global health concern with diverse etiologies and limited treatment options. Ellagic acid (EA), a natural polyphenolic compound, exhibits promising anticancer properties against various GI malignancies. In this article, we have reviewed recent research on the anticancer potential of EA across esophageal, gastric, colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancers. In esophageal cancer, EA inhibits the formation of O6-methylguanine (O6-meGua) adducts induced by carcinogens like N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine (NMBA), thereby suppressing tumor growth. Additionally, EA inhibits STAT3 signaling and stabilizes tumor suppressor proteins, showing potential as an anti-esophageal cancer agent. In gastric cancer, EA regulates multiple pathways involved in cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis, including the p53 and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways. It also demonstrates anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, making it a promising therapeutic candidate against gastric cancer. In colorectal cancer (CRC), EA inhibits cell proliferation, induces apoptosis, and modulates the Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt pathways, suggesting its efficacy in preventing CRC progression. Furthermore, EA has shown promise in pancreatic cancer by inhibiting nuclear factor-kappa B, inducing apoptosis, and suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. In liver cancer, EA exhibits radio-sensitizing effects, inhibits inflammatory pathways, and modulates the tumor microenvironment, offering potential therapeutic benefits against hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies on EA potential in combination therapies and the development of targeted delivery systems are required for enhanced efficacy against gastrointestinal cancers.
Keywords: Chemopreventive; Ellagic acid; Gastrointestinal malignancies; Gastroprotective; Therapeutic resistance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ellagic acid inhibits cell proliferation, migration, and invasion of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells via the Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K/Akt pathways.Acta Biochim Pol. 2023 Feb 11;70(1):109-115. doi: 10.18388/abp.2020_6317. Acta Biochim Pol. 2023. PMID: 36773307
-
Ellagic acid inhibits human pancreatic cancer growth in Balb c nude mice.Cancer Lett. 2013 Sep 1;337(2):210-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.05.009. Epub 2013 May 16. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23684930
-
Ellagic acid inhibits tumor growth and potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 18;10(1):e23931. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23931. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38205284 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted mechanisms of ellagic acid in the treatment of tumors: State-of-the-art.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Sep;165:115132. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115132. Epub 2023 Jul 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37423169 Review.
-
Molecular mechanisms underlying the action of carcinogens in gastric cancer with a glimpse into targeted therapy.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022 Dec;45(6):1073-1117. doi: 10.1007/s13402-022-00715-3. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2022. PMID: 36149600 Review.
Cited by
-
Ellagic Acid and Gut Microbiota: Interactions, and Implications for Health.Food Sci Nutr. 2025 Apr 6;13(4):e70133. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.70133. eCollection 2025 Apr. Food Sci Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40196228 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024. 10.3322/caac.21834. - PubMed
-
- Davoodvandi A, Sadeghi S, Alavi SMA, Alavi SS, Jafari A, Khan H, Aschner M, Mirzaei H, Sharifi M, Asemi Z. The therapeutic effects of berberine for gastrointestinal cancers. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2024;20:152–67. 10.1111/ajco.13941. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

