Impact of high rheumatoid factor levels on treatment outcomes with certolizumab pegol and adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 39222436
- PMCID: PMC11534142
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae435
Impact of high rheumatoid factor levels on treatment outcomes with certolizumab pegol and adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objectives: To assess the impact of baseline RF level on drug concentrations and efficacy of certolizumab pegol [CZP; TNF inhibitor (TNFi) without a crystallizable fragment (Fc)] and adalimumab (ADA; Fc-containing TNFi) in patients with RA.
Methods: The phase 4 EXXELERATE study (NCT01500278) was a 104-week, randomized, single-blind (double-blind until week 12; investigator-blind thereafter), head-to-head study of CZP vs ADA in patients with RA. In this post hoc analysis, we report drug concentration and efficacy outcomes stratified by baseline RF quartile (≤Q3 or >Q3).
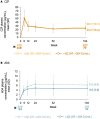
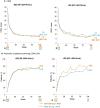
Results: Baseline data by RF quartiles were available for 453 CZP-randomized and 454 ADA-randomized patients (≤Q3: ≤204 IU/ml; >Q3: >204 IU/ml). From week 12, the area under the curve (AUC) of ADA concentration was lower in patients with RF >204 IU/ml vs patients with RF ≤204 IU/ml; the AUC of CZP concentration was similar in patients with RF ≤204 IU/ml and >204 IU/ml. For patients with RF ≤204 IU/ml, disease activity score (DAS28)-CRP was similar between CZP- and ADA-treated patients through week 104. For patients with RF >204 IU/ml, mean DAS28-CRP was lower in CZP- vs ADA-treated patients at week 104. The proportion of patients with RF >204 IU/ml achieving DAS28-CRP low disease activity at week 104 was greater in CZP- vs ADA-treated patients.
Conclusion: CZP was associated with maintained drug concentration and efficacy in patients with RA and high RF and may therefore be a more suitable therapeutic option than TNFis with an Fc fragment in these patients.
Trial registration: Clinicaltrials.gov, http://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT01500278.
Keywords: RA; RF; TNF inhibitor.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


References
-
- Kanmert D, Kastbom A, Almroth G et al. IgG rheumatoid factors against the four human Fc-gamma subclasses in early rheumatoid arthritis (The Swedish TIRA Project). Scand J Immunol 2012;75:115–9. - PubMed
-
- Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y et al. Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:797–808. - PubMed
-
- Vastesaeger N, Xu S, Aletaha D, St Clair EW, Smolen JS. A pilot risk model for the prediction of rapid radiographic progression in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:1114–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

