Immunosuppressant therapy averts rejection of allogeneic FKBP1A-disrupted CAR-T cells
- PMID: 39222637
- PMCID: PMC11489550
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.06.022
Immunosuppressant therapy averts rejection of allogeneic FKBP1A-disrupted CAR-T cells
Abstract
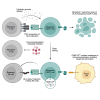
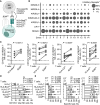
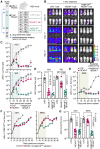
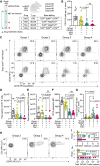
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells from allogeneic donors promise "off-the-shelf" availability by overcoming challenges associated with autologous cell manufacturing. However, recipient immunologic rejection of allogeneic CAR-T cells may decrease their in vivo lifespan and limit treatment efficacy. Here, we demonstrate that the immunosuppressants rapamycin and tacrolimus effectively mitigate allorejection of HLA-mismatched CAR-T cells in immunocompetent humanized mice, extending their in vivo persistence to that of syngeneic humanized mouse-derived CAR-T cells. In turn, genetic knockout (KO) of FKBP prolyl isomerase 1A (FKBP1A), which encodes a protein targeted by both drugs, was necessary to confer CD19-specific CAR-T cells (19CAR) robust functional resistance to these immunosuppressants. FKBP1AKO 19CAR-T cells maintained potent in vitro functional profiles and controlled in vivo tumor progression similarly to untreated 19CAR-T cells. Moreover, immunosuppressant treatment averted in vivo allorejection permitting FKBP1AKO 19CAR-T cell-driven B cell aplasia. Thus, we demonstrate that genome engineering enables immunosuppressant treatment to improve the therapeutic potential of universal donor-derived CAR-T cells.
Keywords: CAR-T cells; base editing; gene editing; immunosuppressants; immunotherapy; universal donor.
Copyright © 2024 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests C.R.M., A.C.M., P.B.B., A.J.C., F.M.M., M.L.W., J.J.R., L.J.C., C.K., F.L., and B.Y. were employees of Beam Therapeutics when the work was conducted and are shareholders in the company. Beam Therapeutics has filed patent applications based on this work.
Figures



References
-
- Wang X., Borquez-Ojeda O., Stefanski J., Du F., Qu J., Chaudhari J., Thummar K., Zhu M., Shen L.B., Hall M., et al. Depletion of high-content CD14+ cells from apheresis products is critical for successful transduction and expansion of CAR T cells during large-scale cGMP manufacturing. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021;22:377–387. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2021.06.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

