Artificial intelligence guided screening for cardiomyopathies in an obstetric population: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 39223284
- PMCID: PMC11485252
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-024-03243-9
Artificial intelligence guided screening for cardiomyopathies in an obstetric population: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Artificial intelligence guided screening for cardiomyopathies in an obstetric population: a pragmatic randomized clinical trial.Nat Med. 2025 May;31(5):1715. doi: 10.1038/s41591-025-03554-5. Nat Med. 2025. PMID: 39905272 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
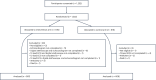
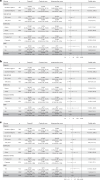
Nigeria has the highest reported incidence of peripartum cardiomyopathy worldwide. This open-label, pragmatic clinical trial randomized pregnant and postpartum women to usual care or artificial intelligence (AI)-guided screening to assess its impact on the diagnosis left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) in the perinatal period. The study intervention included digital stethoscope recordings with point of-care AI predictions and a 12-lead electrocardiogram with asynchronous AI predictions for LVSD. The primary end point was identification of LVSD during the study period. In the intervention arm, the primary end point was defined as the number of identified participants with LVSD as determined by a positive AI screen, confirmed by echocardiography. In the control arm, this was the number of participants with clinical recognition and documentation of LVSD on echocardiography in keeping with current standard of care. Participants in the intervention arm had a confirmatory echocardiogram at baseline for AI model validation. A total of 1,232 (616 in each arm) participants were randomized and 1,195 participants (587 intervention arm and 608 control arm) completed the baseline visit at 6 hospitals in Nigeria between August 2022 and September 2023 with follow-up through May 2024. Using the AI-enabled digital stethoscope, the primary study end point was met with detection of 24 out of 587 (4.1%) versus 12 out of 608 (2.0%) patients with LVSD (intervention versus control odds ratio 2.12, 95% CI 1.05-4.27; P = 0.032). With the 12-lead AI-electrocardiogram model, the primary end point was detected in 20 out of 587 (3.4%) versus 12 out of 608 (2.0%) patients (odds ratio 1.75, 95% CI 0.85-3.62; P = 0.125). A similar direction of effect was observed in prespecified subgroup analysis. There were no serious adverse events related to study participation. In pregnant and postpartum women, AI-guided screening using a digital stethoscope improved the diagnosis of pregnancy-related cardiomyopathy. ClinicalTrials.gov registration: NCT05438576.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.A.A. is supported by the Mayo Clinic BIRCWH program funded by the NIH (grant no. K12 AR084222). The content of the article is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH. Z.I.A. is a co-inventor of several AI algorithms (including screening for low LVEF, QT tool, aortic stenosis and atrial fibrillation detection during normal sinus rhythm). These have been licensed to Anumana, AliveCor and Eko. The Mayo Clinic and Z.I.A. may benefit from their commercialization. Z.I.A. is a member of the scientific advisory board for Anumana, an AI company, receives stock options for being an inventor of the ejection fraction algorithm and is a consultant for Anumana, AliveCor and XAI.health. P.A.F. is a co-inventor of several AI algorithms (including screening for low LVEF, QT tool, aortic stenosis and atrial fibrillation detection during normal sinus rhythm). These have been licensed to Anumana, AliveCor and Eko. The Mayo Clinic and P.A.F. may benefit from their commercialization. P.A.F. is a member of the scientific advisory board for Anumana, an AI company. F.L.J. in conjunction with the Mayo Clinic has filed patents related to the application of AI to ECG for diagnosis and risk stratification. F.L.J. is a member of the scientific advisory board for Anumana, an AI company. P.A.N. and the Mayo Clinic have filed patents related to the application of AI to ECG for diagnosis and risk stratification and have licensed several AI-ECG algorithms to Anumana. P.A.N. and the Mayo Clinic are involved in potential equity/royalty relationship with AliveCor. P.A.N. is a study investigator in an ablation trial sponsored by Medtronic. P.A.N. also has served on an expert advisory panel for OptumLabs. Y.B.T. has sponsored research grants from HeraMed, Mitre Corp (MSTORC development grant) and the COVID-19 Interactive Care Plan. Y.B.T. also receives know-how royalties for co-development of HeraBEAT from HeraMed Corp. R.E.C. is a scientific advisor for Anumana, an AI-driven health technology company commercializing ECG-based AI solutions. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Gunderson, E. P. et al. Epidemiology of peripartum cardiomyopathy: incidence, predictors, and outcomes. Obstet. Gynecol.118, 583–591 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Karaye, K. M. et al. Clinical features and outcomes of peripartum cardiomyopathy in nigeria. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol.76, 2352–2364 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Isogai, T. & Kamiya, C. A. Worldwide incidence of peripartum cardiomyopathy and overall maternal mortality. Int. Heart J.60, 503–511 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

