Advanced pulmonary tuberculosis in Alameda County: Ten-year incidence and risk factors
- PMID: 39224114
- PMCID: PMC11367100
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2024.100475
Advanced pulmonary tuberculosis in Alameda County: Ten-year incidence and risk factors
Abstract
Background: Advanced pulmonary tuberculosis (APT) may reflect delays in tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis and contribute to ongoing disease transmission and poor outcomes. We characterized trends and factors associated with APT over ten years in a high TB-burden county within the United States.
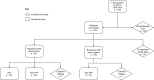
Methods: We evaluated microbiologically and clinically confirmed TB cases reported to the Alameda County Public Health Department during 2010-2019. APT was defined as the presence of cavitation on chest imaging and positive acid-fast bacilli sputum smear. Over the ten-year period, we determined overall incidence and annual trends, and conducted multivariable logistic regression to identify sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with APT.
Results: We included 997 cases with pulmonary TB, of which 128 (12.8 %) had APT. The 10-year incidence of APT was 8.8 cases per 100,000, with no significant change in proportion over time. The median age of cases with APT were 50 years (IQR 32-61), 68 % were male, and 78.9 % were non-US-born. On multivariable assessment, APT cases were more likely than non-APT cases to use drugs in the past year (aOR 2.43, 95 % CI 1.10-35.09), to have diabetes (aOR 2.51, 95 % CI: 1.59-3.96), and be HIV negative (aOR 9.32 versus HIV positive, 95 % CI 1.87-169.77). While US nativity was not significantly associated with APT, it was an effect modifier. In stratified analysis, APT was more likely among those with drug-use in the last year among US-born, while diabetes was associated with APT among non-US-born individuals.
Conclusions: APT remains a substantial proportion of TB cases. Efforts to increase awareness and access to care are needed for key risk groups including those with recent drug use or diabetes, with consideration of cultural and linguistic factors given differences by US nativity.
Keywords: Delayed diagnosis; Epidemiology; Surveillance; Tuberculosis; United States.
© 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Xpert® MTB/RIF assay for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014 Jan 21;2014(1):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Jun 07;6:CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub4. PMID: 24448973 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Behavioral interventions to reduce risk for sexual transmission of HIV among men who have sex with men.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008 Jul 16;(3):CD001230. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001230.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008. PMID: 18646068
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis Prevention, Control, and Elimination.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30020618 Free Books & Documents.
Cited by
-
Adenosine Deaminase and Systemic Immune Inflammatory Index-A Biomarker Duet Signature of Pulmonary Tuberculosis Severity.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jun 17;61(6):1096. doi: 10.3390/medicina61061096. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 40572784 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wallace R.M., Kammerer J.S., Iademarco M.F., Althomsons S.P., Winston C.A., Navin T.R. Increasing proportions of advanced pulmonary tuberculosis reported in the United States: are delays in diagnosis on the rise? Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:1016–1022. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200901-0059OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

