A randomized controlled trial protocol for the introduction of a multidisciplinary individualized nutritional intervention in children with cerebral palsy
- PMID: 39224169
- PMCID: PMC11366897
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101343
A randomized controlled trial protocol for the introduction of a multidisciplinary individualized nutritional intervention in children with cerebral palsy
Abstract
Introduction: Children with Cerebral Palsy (CP) encounter substantial nutritional challenges that impair their health and quality of life. Despite the importance of nutrition in managing CP and the recognition of physiological, behavioral, and social causes of malnutrition, research on the effectiveness of individualized nutritional interventions developed and supported by multidisciplinary teams is scarce.
Aim: The study will evaluate the impact of an individualized nutritional intervention developed and supported by a multidisciplinary team on the anthropometric outcomes and overall health of children with CP.
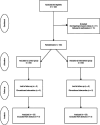
Methods: A single-center, randomized controlled trial, conducted at the Medical University of Varna, Bulgaria, will enroll 100 children aged 2-12 years and diagnosed with CP. Participants will be randomly assigned to either an intervention group, receiving comprehensive structured dietary assessment and individualized nutrition plan developed by a multidisciplinary team of experts, or to a standard care group. Outcomes assessed will focus on anthropometric measures of nutritional status, but also include health outcomes, child development and clinical assessments, and quality of life indicators.
Ethics: Ethical approval for this study has been obtained from the Medical Ethics Committee at the Medical University of Varna (Protocol No. 134 dated 20.07.2023).
Conclusion: This study will assess the benefits of a multidisciplinary, individualized nutritional intervention for children with CP. The findings will have implications for clinical guidelines and interventions aiming to improve their care and quality of life.
Keywords: Cerebral palsy; Individualized; Intervention; Multidisciplinary; Nutrition.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Fragale N., Navarre N., Rogers J. In: Cerebral Palsy. Miller F., Bachrach S., Lennon N., O'Neil M., editors. Springer International Publishing; Cham: 2019. General nutrition for children with cerebral palsy; pp. 1–10. - DOI
-
- Jahan I., Sultana R., Muhit M., Akbar D., Karim T., Al Imam M.H., Das M.C., Smithers-Sheedy H., McIntyre S., Badawi N., Khandaker G. Nutrition interventions for children with cerebral palsy in low-and middle-income countries: a scoping review. Nutrients. 2022;14 doi: 10.3390/nu14061211. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- CDC Help children maintain healthy weight [WWW document] Cent. Dis. Control Prev. 2023 https://www.cdc.gov/healthyweight/children/index.html URL.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

