Reconstruction of Complex Upper Extremity Wounds With Novosorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix Versus Integra Collagen-Chondroitin Silicone: A Cost Analysis
- PMID: 39224413
- PMCID: PMC11367154
Reconstruction of Complex Upper Extremity Wounds With Novosorb Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix Versus Integra Collagen-Chondroitin Silicone: A Cost Analysis
Abstract
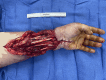
Background: Reconstruction of upper extremity wounds with dermal matrices can reduce the length of hospitalization and surgical complexity without compromising functional outcomes. We aimed to compare costs between Novosorb biodegradable temporizing matrix (BTM) and Integra collagen-chondroitin silicone (CCS) bilayer.
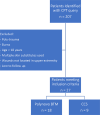
Methods: A chart review was performed for patients with isolated upper extremity traumatic wounds who underwent reconstruction with either BTM or CCS between January 2017 and May 2022. Demographic data, surgical procedures, outcomes, and costs were collected for analysis.
Results: Twenty-seven patients were included: 18 BTM and 9 CCS. There were no differences in age, sex, wound size, or dermal template size. Skin grafting was required less frequently in BTM compared with CCS (44.4% vs 55.6%, P = .013). Time to skin graft was longer in the BTM group (43.4 days vs 21.4 days, P = .002). The BTM group experienced fewer complications (33.3% vs 55.6%, P = .002). The mean number of secondary procedures required after template placement was 0.67 in BTM compared with 1.56 in CCS, P = .049. When factoring in the cost of product, the cost of reconstruction with BTM was significantly lower than CCS ($1361.92 vs $3185.71, P = .049).
Conclusions: Novosorb BTM is a more cost-effective option when compared with CCS for reconstruction of upper extremity soft tissue defects.
Keywords: Dermal Matrix; Reconstruction; Trauma; Upper Extremity; Wound.
© 2024 HMP Global. All Rights Reserved. Any views and opinions expressed are those of the author(s) and/or participants and do not necessarily reflect the views, policy, or position of ePlasty or HMP Global, their employees, and affiliates.
Figures

References
-
- Brusselaers N, Pirayesh A, Hoeksema H, et al. Skin replacement in burn wounds. J Trauma. 2010;68(2):490-501. doi:10.1097/TA.0b013e3181c9c074 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chim H, Ng ZY, Carlsen BT, Mohan AT, Saint-Cyr M. Soft tissue coverage of the upper extremity: an overview. Hand Clin. 2014;30(4):459-vi. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2014.08.002 10.1016/j.hcl.2014.08.002 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Miller EA, Friedrich J. Soft tissue coverage of the hand and upper extremity: the reconstructive elevator. J Hand Surg Am. 2016;41(7):782-792. doi:10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.04.020 10.1016/j.jhsa.2016.04.020 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nandi S, Maschke S, Evans PJ, Lawton JN. The stiff elbow. Hand (N Y). 2009;4(4):368-379. doi:10.1007/s11552-009-9181-z 10.1007/s11552-009-9181-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
