Phospholipase A2 receptor-negative membranous nephropathy presenting as a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 39224761
- PMCID: PMC11367585
- DOI: 10.1177/2050313X241279696
Phospholipase A2 receptor-negative membranous nephropathy presenting as a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease
Abstract
IgG4-related disease is a fibroinflammatory condition characterized by dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells affecting multiple organs. Though the most common renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease is tubulointerstitial nephritis, it can rarely present as secondary membranous nephropathy. We present a case of a 75-year-old male with phospholipase A2 receptor-negative membranous nephropathy as an atypical manifestation of IgG4-related disease. The patient presented with nephrotic syndrome and was found to have elevated serum IgG4 levels and IgG4-positive plasma cells in the kidney biopsy. He was successfully treated with corticosteroids and rituximab, resulting in significant improvement in proteinuria and normalization of IgG4 levels. This case highlights the importance of considering IgG4-related disease in patients with phospholipase A2 receptor-negative membranous nephropathy, especially in those with a history of other organ involvement. Early recognition and treatment of IgG4-related disease are crucial to prevent progressive kidney damage and improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: IgG4-related disease; PLA2R-negative; rituximab; secondary membranous nephropathy; tubulointerstitial nephritis.
© The Author(s) 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
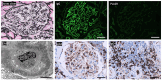
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined membranous nephropathy and tubulointerstitial nephritis as a rare renal manifestation of IgG4-related disease: a case-based literature review.CEN Case Rep. 2018 May;7(1):137-142. doi: 10.1007/s13730-018-0311-8. Epub 2018 Feb 1. CEN Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 29388171 Free PMC article.
-
PLA2R-positive membranous nephropathy in IgG4-related disease.BMC Nephrol. 2024 Feb 23;25(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12882-024-03511-3. BMC Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38395839 Free PMC article.
-
Low-density lipoprotein apheresis for PLA2R-related membranous glomerulonephritis accompanied by IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis.CEN Case Rep. 2020 Nov;9(4):395-403. doi: 10.1007/s13730-020-00494-6. Epub 2020 Jun 16. CEN Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32557252 Free PMC article.
-
ALECT2 amyloidosis with concurrent IgG4-related interstitial nephritis, membranous nephropathy and diabetic kidney disease: a case report and literature review.J Nephrol. 2024 Nov;37(8):2363-2369. doi: 10.1007/s40620-024-01924-9. Epub 2024 Apr 17. J Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38630340 Review.
-
IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) with membranous nephropathy as its initial manifestation: report of one case and literature review.BMC Nephrol. 2019 Jul 16;20(1):263. doi: 10.1186/s12882-019-1419-6. BMC Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31311519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med 2012; 366(6): 539–551. - PubMed
-
- Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N, et al.. Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int 2010; 78(10): 1016–1023. - PubMed
-
- Alexander MP, Larsen CP, Gibson IW, et al.. Membranous glomerulonephritis is a manifestation of IgG4-related disease. Kidney Int 2013; 83(3): 455–462. - PubMed

