Phase Ib/II study on the safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of pegylated irinotecan (JK1201I) as second-line monotherapy for patients with small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 39225504
- PMCID: PMC11369986
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.70059
Phase Ib/II study on the safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of pegylated irinotecan (JK1201I) as second-line monotherapy for patients with small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of multiple doses of pegylated irinotecan (JK1201I) as a second-line monotherapy for treating small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients.
Methods: According to the "3 + 3" dose-escalation principle, patients received intravenous JK1201I at 180 or 220 mg/m2 once every 3 weeks for four cycles. Progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), median progression-free survival (mPFS), and median overall survival (mOS) were evaluated. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to analyze PFS and overall OS. Brookmeyer and Crowley's method was used for mPFS and mOS.
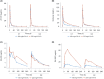
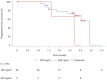
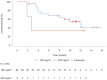
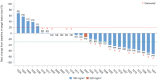
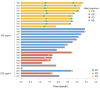
Results: This study included 29 patients with stage III-IV SCLC (stage IIIa, n = 1; stage IIIb, n = 1; and stage IV, n = 27). Of these, 26 patients were enrolled in the 180 mg/m2 dose group, and 3 patients were enrolled in the 220 mg/m2 dose group. No dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) was noted during the first 28 days of treatment. Grade 3 or higher adverse events were recorded in the 180 mg/m2 group, including diarrhea (11.5%, 3/26), neutropenia (7.7%, 2/26), and leukopenia (7.7%, 2/26). In the 220 mg/m2 group, one patient (33.3%, 1/3) experienced neutropenia or leukopenia. In the 180 mg/m2 group, 38.5% (10/26) of patients achieved an objective response rate (ORR), with a disease control rate (DCR) of 73.1% (19/26). The mPFS and mOS were 3.4 and 12.1 months, respectively. In the 220 mg/m2 group, one patient had stable disease, and one had progressive disease (PD). The ORR, DCR, mPFS, and mOS were 0% (0/3) and 33.3% (1/3), 2.7 months and 2.7 months, respectively.
Conclusion: JK1201I exhibits promising efficacy and relatively low toxicities as a second-line monotherapy for SCLC, warranting further large-scale clinical studies to evaluate its efficacy in greater detail.
Keywords: overall survival; safety; second‐line monotherapy; small‐cell lung cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RESILIENT Part 2: A Randomized, Open-Label Phase III Study of Liposomal Irinotecan Versus Topotecan in Adults With Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2024 Jul 1;42(19):2317-2326. doi: 10.1200/JCO.23.02110. Epub 2024 Apr 22. J Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38648575 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
RESILIENT part 1: a phase 2 dose-exploration and dose-expansion study of second-line liposomal irinotecan in adults with small cell lung cancer.Cancer. 2022 May 1;128(9):1801-1811. doi: 10.1002/cncr.34123. Epub 2022 Feb 23. Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35195913 Clinical Trial.
-
[Analysis of the Efficacy of Irinotecan in the Second-line Treatment of Refractory and Relapsed Small Cell Lung Cancer].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021 Mar 20;24(3):167-172. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2021.103.04. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 33819966 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Efficacy and toxicity of lurbinectedin in subsequent systemic therapy of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2024 Nov 4;24(1):1351. doi: 10.1186/s12885-024-13104-w. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39497053 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone as first-line treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Dec;11(12):3536-3546. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13698. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33058504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ardizzoni A, Hansen H, Dombernowsky P, et al. Topotecan, a new active drug in the second‐line treatment of small‐cell lung cancer: a phase II study in patients with refractory and sensitive disease. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of cancer early clinical studies group and new drug development office, and the lung cancer cooperative group. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15(5):2090‐2096. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien ME, Ciuleanu TE, Tsekov H, et al. Phase III trial comparing supportive care alone with supportive care with oral topotecan in patients with relapsed small‐cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(34):5441‐5447. - PubMed
-
- Kondo R, Watanabe S, Shoji S, et al. A phase II study of Irinotecan for patients with previously treated small‐cell lung cancer. Oncology. 2018;94(4):223‐232. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

