Distal femoral fractures: periprosthetic fractures have four times more complications than non-periprosthetic fractures and cerclage should be avoided: retrospective analysis of 206 patients
- PMID: 39225851
- PMCID: PMC11371989
- DOI: 10.1186/s10195-024-00782-2
Distal femoral fractures: periprosthetic fractures have four times more complications than non-periprosthetic fractures and cerclage should be avoided: retrospective analysis of 206 patients
Abstract
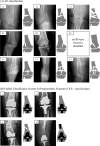
Background: Distal femoral fractures account for less than 1% of all fractures. The therapy of choice is usually surgical stabilization. Despite advances in implant development over the past few years, complication rate remains comparatively high. The aim of this study is to analyze our results with plate fixation of distal femoral fractures with a focus on complication and fracture healing rates.
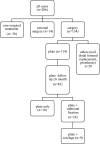
Methods: In this retrospective cohort study, patients (> 18 years) with distal femoral fractures treated at an urban level I trauma center between 2015 and 2022 were analyzed.
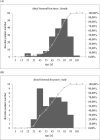
Results: In total, 206 patients (167 female, 39 male) with an average age of 75 (SD 16) years were diagnosed with a fracture of the distal femur. One hundred fourteen of these patients were treated surgically by means of plate osteosynthesis. In 13 cases (11.41%), a revision procedure had to be performed. The indication for surgical revision was mechanical failure in eight cases (7.02%) and septic complication in five cases (4.39%). Periprosthetic fractures were more likely to cause complications overall (19.6% versus 4.76%) and further included all documented septic complications. The analysis of modifiable surgical factors in the context of plate osteosynthesis showed higher complication rates for cerclage in the fracture area compared with plate-only stabilizations (44.44% versus 22.22%).
Conclusions: The data show an increased amount of revisions and a significantly higher number of septic complications in the treatment of periprosthetic fractures of the distal femur compared with non-periprosthetic fractures. The detected combination of plates together with cerclage was associated with higher complication rates. Level of evidence Level III retrospective comparative study.
Keywords: Cerclage; Complication rate; Distal femoral fracture; Plate osteosynthesis.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Treatment of Periprosthetic Distal Femoral Fractures].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2019;86(3):205-211. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2019. PMID: 31333185 Czech.
-
[Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Total Hip Replacement: Our Results and Treatment Complications].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2017;84(1):52-58. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2017. PMID: 28253947 Czech.
-
[Osteosynthesis for periprosthetic supracondylar fracture above a total knee arthroplasty using a locking compression plate].Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009 Dec;76(6):473-8. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2009. PMID: 20067694 Czech.
-
Distal Femoral Replacement versus Operative Fixation for Periprosthetic Distal Femur Fractures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Arthroplasty. 2023 Jul;38(7 Suppl 2):S450-S458. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2023.01.044. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Arthroplasty. 2023. PMID: 36738864
-
Equivalent union rates between intramedullary nail and locked plate fixation for distal femur periprosthetic fractures - a systematic review.Injury. 2020 Apr;51(4):1062-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2020.02.043. Epub 2020 Feb 16. Injury. 2020. PMID: 32115204
Cited by
-
Management of open periprosthetic distal femoral fracture using a novel hybrid technique combining Masquelet and DAIR procedure: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025 Aug;133:111511. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2025.111511. Epub 2025 Jun 15. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 40532546 Free PMC article.
-
Implant removal: benefits and drawbacks - Results of a survey with five hundred participants from the Italian Society of Orthopedic Surgery and Traumatology (SIOT) and comparison with other international trends.Int Orthop. 2025 Aug;49(8):1775-1787. doi: 10.1007/s00264-025-06564-7. Epub 2025 May 26. Int Orthop. 2025. PMID: 40415005 Free PMC article.
-
Double plating versus nail-plate construct in AO 33C distal femur fractures: treatment choice affects knee alignment, clinical outcomes, and quality of life-a multicenter study.J Orthop Traumatol. 2025 Apr 2;26(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s10195-025-00834-1. J Orthop Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 40175637 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

