In-depth Analysis of the HIV Reservoir Confirms Effectiveness and Safety of Dolutegravir/Lamivudine in a Phase 4 Randomized Controlled Switch Trial (RUMBA)
- PMID: 39226296
- PMCID: PMC11793038
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiae405
In-depth Analysis of the HIV Reservoir Confirms Effectiveness and Safety of Dolutegravir/Lamivudine in a Phase 4 Randomized Controlled Switch Trial (RUMBA)
Abstract
Background: Reducing the number of active compounds for lifelong human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) treatment is of interest, especially to reduce potential long-term side effects. So far, available data assessing viral control support the robustness and safety of 2DR (2-drug regimen) antiretroviral therapy compared to 3DR. However, further in-depth investigations of the viral reservoirs are mandatory to guarantee long-term safety of these regimens regarding stable intact HIV-1 DNA copies, HIV-1 RNA transcripts, and sustained immunological control.
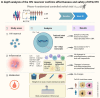
Methods: The RUMBA study is the first prospective randomized controlled trial evaluating the impact of switch from 3DR to 2DR on the viral reservoir. Participants on any stable second-generation integrase strand transfer inhibitor-based 3DR regimen with HIV-1 RNA < 50 copies/mL plasma for at least 3 months were randomized to switch to dolutegravir/lamivudine (DTG/3TC, n = 89) or to switch or stay on bictegravir/emtricitabine/tenofovir alafenamide (B/F/TAF, n = 45). After 48 weeks, virological, immunological, and metabolic parameters were evaluated.
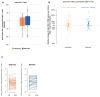
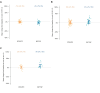
Results: We did not observe a significant difference in change over time in the mean number of intact HIV-1 DNA copies/million CD4+ T cells with DTG/3TC compared to B/F/TAF. There was no evidence in this study that switching to DTG/3TC increased the active reservoir by HIV-1 transcription. No significant changes in proinflammatory cytokines or major immune cell subsets were observed. Changes in exhaustion and activation of specific cellular subsets were small and bidirectional. Metabolic outcomes are similar between the treatment regimens.
Conclusions: This study confirms the safety of DTG/3TC compared to B/F/TAF through viral control after in-depth investigations of the intact HIV-1 reservoir, HIV-1 transcription, and inflammatory markers.
Clinical trials registration: NCT04553081.
Keywords: HIV-1 reservoir; dual ART; inflammation; metabolic health; switch randomized controlled trial.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. M. D. S. has been granted speakers fees from Gilead Sciences, ViiV Healthcare, and MSD; and has received grants from MSD, ViiV Healthcare, and Gilead Sciences to conduct independent investigator-initiated research in the HIV field. L. V. has been granted speaker fees and support for research projects by ViiV Healthcare, Gilead Sciences, and Johnson and Johnson over the past 5 years. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
References
-
- Cahn P, Madero JS, Arribas JR, et al. Dolutegravir plus lamivudine versus dolutegravir plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and emtricitabine in antiretroviral-naive adults with HIV-1 infection (GEMINI-1 and GEMINI-2): week 48 results from two multicentre, double-blind, randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trials. Lancet 2019; 393:143–55. - PubMed
-
- Llibre JM, Brites C, Cheng CY, et al. Efficacy and safety of switching to the 2-drug regimen dolutegravir/lamivudine versus continuing a 3- or 4-drug regimen for maintaining virologic suppression in adults living with human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1): week 48 results from the phase 3, noninferiority SALSA randomized trial. Clin Infect Dis 2023; 76:720–9. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Llibre JM, Hung CC, Brinson C, et al. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of dolutegravir-rilpivirine for the maintenance of virological suppression in adults with HIV-1: phase 3, randomised, non-inferiority SWORD-1 and SWORD-2 studies. Lancet 2018; 391:839–49. - PubMed
-
- van Wyk J, Ajana F, Bisshop F, et al. Efficacy and safety of switching to dolutegravir/lamivudine fixed-dose 2-drug regimen vs continuing a tenofovir alafenamide-based 3- or 4-drug regimen for maintenance of virologic suppression in adults living with human immunodeficiency virus type 1: phase 3, randomized, noninferiority TANGO study. Clin Infect Dis 2020; 71:1920–9. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

