Accuracy of CAD4TB (Computer-Aided Detection for Tuberculosis) on paediatric chest radiographs
- PMID: 39227074
- PMCID: PMC11540982
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00811-2024
Accuracy of CAD4TB (Computer-Aided Detection for Tuberculosis) on paediatric chest radiographs
Abstract
Background: Computer-aided detection (CAD) systems hold promise for improving tuberculosis (TB) detection on digital chest radiographs. However, data on their performance in exclusively paediatric populations are scarce.
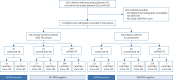
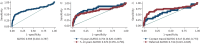
Methods: We conducted a retrospective diagnostic accuracy study evaluating the performance of CAD4TBv7 (Computer-Aided Detection for Tuberculosis version 7) using digital chest radiographs from well-characterised cohorts of Gambian children aged <15 years with presumed pulmonary TB. The children were consecutively recruited between 2012 and 2022. We measured CAD4TBv7 performance against a microbiological reference standard (MRS) of confirmed TB, and also performed Bayesian latent class analysis (LCA) to address the inherent limitations of the MRS in children. Diagnostic performance was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) and point estimates of sensitivity and specificity.
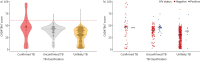
Results: A total of 724 children were included in the analysis, with confirmed TB in 58 (8%), unconfirmed TB in 145 (20%) and unlikely TB in 521 (72%). Using the MRS, CAD4TBv7 showed an AUROC of 0.70 (95% CI 0.60-0.79), and demonstrated sensitivity and specificity of 19.0% (95% CI 11-31%) and 99.0% (95% CI 98.0-100.0%), respectively. Applying Bayesian LCA with the assumption of conditional independence between tests, sensitivity and specificity estimates for CAD4TBv7 were 42.7% (95% CrI 29.2-57.5%) and 97.9% (95% CrI 96.6-98.8%), respectively. When allowing for conditional dependence between culture and Xpert assay, CAD4TBv7 demonstrated a sensitivity of 50.3% (95% CrI 32.9-70.0%) and specificity of 98.0% (95% CrI 96.7-98.9%).
Conclusion: Although CAD4TBv7 demonstrated high specificity, its suboptimal sensitivity underscores the crucial need for optimisation of CAD4TBv7 for detecting TB in children.
Copyright ©The authors 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Comment in
-
TB or not TB: does AI have an answer for children?Eur Respir J. 2024 Nov 7;64(5):2401709. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01709-2024. Print 2024 Nov. Eur Respir J. 2024. PMID: 39510596 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2023. www.who.int/teams/global-tuberculosis-programme/tb-reports/global-tuberc... Date last accessed: 25 January 2024.
-
- World Health Organization . Chest radiography in tuberculosis detection: summary of current WHO recommendations and guidance on programmatic approaches. 2016. https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/252424 Date last accessed: 25 January 2024.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
