The PS4-likelihood ratio calculator: flexible allocation of evidence weighting for case-control data in variant classification
- PMID: 39227160
- PMCID: PMC11503184
- DOI: 10.1136/jmg-2024-110034
The PS4-likelihood ratio calculator: flexible allocation of evidence weighting for case-control data in variant classification
Abstract
Background: The 2015 American College of Medical Genetics/Association of Molecular Pathology (ACMG/AMP) variant classification framework specifies that case-control observations can be scored as 'strong' evidence (PS4) towards pathogenicity.
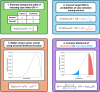
Methods: We developed the PS4-likelihood ratio calculator (PS4-LRCalc) for quantitative evidence assignment based on the observed variant frequencies in cases and controls. Binomial likelihoods are computed for two models, each defined by prespecified OR thresholds. Model 1 represents the hypothesis of association between variant and phenotype (eg, OR≥5) and model 2 represents the hypothesis of non-association (eg, OR≤1).
Results: PS4-LRCalc enables continuous quantitation of evidence for variant classification expressed as a likelihood ratio (LR), which can be log-converted into log LR (evidence points). Using PS4-LRCalc, observed data can be used to quantify evidence towards either pathogenicity or benignity. Variants can also be evaluated against models of different penetrance. The approach is applicable to balanced data sets generated for more common phenotypes and smaller data sets more typical in very rare disease variant evaluation.
Conclusion: PS4-LRCalc enables flexible evidence quantitation on a continuous scale for observed case-control data. The converted LR is amenable to incorporation into the now widely used 2018 updated Bayesian ACMG/AMP framework.
Keywords: Genetic Testing; Genetic Variation; Genetics; Genetics, Population.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2024. Re-use permitted under CC BY. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- ClinGen SVI recommendation for in trans criterion (pm3) - version 1.0. 2019
-
- ClinGen ClinGen sequence variant interpretation recommendation for de novo criteria (ps2/pm6) – version 1.1. 2018
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
