Citrullination modulation stabilizes HIF-1α to promote tumour progression
- PMID: 39227578
- PMCID: PMC11372217
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-51882-w
Citrullination modulation stabilizes HIF-1α to promote tumour progression
Abstract
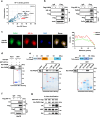
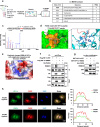
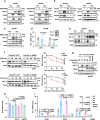
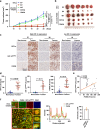
Citrullination plays an essential role in various physiological or pathological processes, however, whether citrullination is involved in regulating tumour progression and the potential therapeutic significance have not been well explored. Here, we find that peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) directly interacts with and citrullinates hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) at R698, promoting HIF-1α stabilization. Mechanistically, PADI4-mediated HIF-1αR698 citrullination blocks von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) binding, thereby antagonizing HIF-1α ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation. We also show that citrullinated HIF-1αR698, HIF-1α and PADI4 are highly expressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) tumour tissues, suggesting a potential correlation between PADI4-mediated HIF-1αR698 citrullination and cancer development. Furthermore, we identify that dihydroergotamine mesylate (DHE) acts as an antagonist of PADI4, which ultimately suppresses tumour progression. Collectively, our results reveal citrullination as a posttranslational modification related to HIF-1α stability, and suggest that targeting PADI4-mediated HIF-1α citrullination is a promising therapeutic strategy for cancers with aberrant HIF-1α expression.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 82341013/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82130087/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 92357301/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82103186/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82273221/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

