Adrenal tumours in patients with pathogenic APC mutations: a retrospective study
- PMID: 39227904
- PMCID: PMC11370095
- DOI: 10.1186/s13053-024-00289-1
Adrenal tumours in patients with pathogenic APC mutations: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: Adrenal tumours are associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP). In the literature, most studies use the clinical definition of FAP (more than 100 adenomatous polyps found in endoscopic studies). However, not all patients that meet clinical criteria for FAP carry pathogenic mutations in the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene, as there is genetic heterogeneity responsible for FAP with the polyposis sometimes explained by genetic and environmental factors other than pathogenic APC mutations. Reciprocally, not all the patients with pathogenic APC variants will fulfil the classic criteria of FAP.
Objective: This study aims to investigate the characteristics of adrenal tumours in patients with pathogenic or likely pathogenic APC variants and explore the hormonal function of these patients.
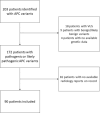
Method: This is a retrospective cohort study. Patients with pathogenic or likely pathogenic APC variants were recruited and their radiological assessments were reviewed. Patient demographic data, APC variants, adrenal mass characteristics and hormonal testing results were collected.
Result: The prevalence of adrenal mass was 26.7% (24/90) among patients with pathogenic or likely pathogenic APC variants. Using the classic definition, the prevalence was 32.4% (22/68). Four patients had adrenal hormone testing, two of which had Conn's syndrome and two had nonspecific subclinical results.
Conclusion: In our cohort, the prevalence of adrenal tumours among patients with pathogenic and likely pathogenic APC mutations is at least twice to three times higher than the general population prevalence reported from international population-based studies. The hormonal functions of patients with pathogenic APC variants and adrenal tumours can be investigated with routine testing in further research.
Keywords: APC; Adrenal tumour; Colorectal cancer; Familial adenomatous polyposis; Genetics.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Germline mutations of the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) gene in Algerian familial adenomatous polyposis cohort: first report.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 May;49(5):3823-3837. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07228-0. Epub 2022 Feb 10. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35142982
-
Novel and reported APC germline mutations in Chinese patients with familial adenomatous polyposis.Gene. 2016 Feb 15;577(2):187-92. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.11.034. Epub 2015 Nov 25. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26625971
-
Gastric polyposis and desmoid tumours as a new familial adenomatous polyposis clinical variant associated with APC mutation at the extreme 3'-end.J Med Genet. 2020 May;57(5):356-360. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106299. Epub 2019 Oct 7. J Med Genet. 2020. PMID: 31591141 Free PMC article.
-
Familial adenomatous polyposis.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009 Oct 12;4:22. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-22. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009. PMID: 19822006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
APC germline mutations in individuals being evaluated for familial adenomatous polyposis: a review of the Mayo Clinic experience with 1591 consecutive tests.J Mol Diagn. 2013 Jan;15(1):31-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2012.07.005. Epub 2012 Nov 14. J Mol Diagn. 2013. PMID: 23159591 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous