Efficacy of modified anterior maxillary segmental distraction osteogenesis based on 3D visualisation for the treatment of maxillary hypoplasia among adolescents with cleft lip and palate
- PMID: 39227941
- PMCID: PMC11370301
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-024-04828-z
Efficacy of modified anterior maxillary segmental distraction osteogenesis based on 3D visualisation for the treatment of maxillary hypoplasia among adolescents with cleft lip and palate
Abstract
Background: This study evaluates a three-dimensional (3D) visualisation design combined with customized surgical guides to assist anterior maxillary segmental distraction osteogenesis (AMSDO) in correcting maxillary hypoplasia in adolescents with cleft lip and palate (CLP), focusing on treatment outcomes, satisfaction and the validity of 3D planning.
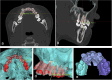
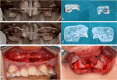
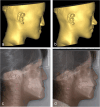
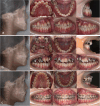
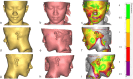
Methods: This retrospective cohort study was conducted at a single hospital in China. Between January 2020 and December 2023, 12 adolescents with CLP with maxillary hypoplasia were included. An advanced 3D simulation was used to convey the treatment strategy to the patients and their families. A customized surgical guide and distraction osteogenesis device were designed. Cephalometric analysis evaluated AMSDO changes and long-term stability. Patient satisfaction was assessed. The Chinese version of the Child Oral Health Impact Profile was used to evaluate the children's oral health-related quality of life before and after treatment. The postoperative outcomes were compared with the planned outcomes by superimposing the actual postoperative data onto the simulated soft tissue models and calculating the linear and angular differences between them.
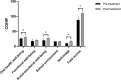
Results: One patient experienced postoperative gingivitis, yielding an 8.33% complication rate. Most patients (83.33%) were highly satisfied with the target position, with the rest content. Cephalometric analysis showed significant improvements in various indices post-traction. Quality-of-life scores significantly improved post-treatment. The discrepancies in facial soft tissue between the simulated and actual results were within clinically satisfactory ranges.
Conclusions: Digitally designed surgical guides effectively treat maxillary hypoplasia in adolescents with CLP, ensuring stability, reducing complications, reducing dependency on operator experience, and enhancing satisfaction and health outcomes. Although the simulated results were clinically acceptable, it is important to inform patients of potential variations in the predicted soft tissue.
Keywords: Anterior maxillary segmental distraction osteogenesis (AMSDO); Child oral health impact profile (COHIP); Cleft lip and palate (CLP); Customized 3D-printed surgical splints; Maxillary hypoplasia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Richardson S, Selvaraj D, Khandeparker RV, Seelan NS, Richardson S. Tooth-borne anterior maxillary distraction for cleft maxillary hypoplasia: our experience with 147 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;74(2504):e1-2504.e14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

