Trends and insights in dengue virus research globally: a bibliometric analysis (1995-2023)
- PMID: 39227968
- PMCID: PMC11370300
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05561-5
Trends and insights in dengue virus research globally: a bibliometric analysis (1995-2023)
Abstract
Background: Dengue virus (DENV) is the most widespread arbovirus. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared dengue one of the top 10 global health threats in 2019. However, it has been underrepresented in bibliometric analyses. This study employs bibliometric analysis to identify research hotspots and trends, offering a comprehensive overview of the current research dynamics in this field.
Results: We present a report spanning from 1995 to 2023 that provides a unique longitudinal analysis of Dengue virus (DENV) research, revealing significant trends and shifts not extensively covered in previous literature. A total of 10,767 DENV-related documents were considered, with a notable increase in publications, peaking at 747 articles in 2021. Plos Neglected Tropical Diseases has become the leading journal in Dengue virus research, publishing 791 articles in this field-the highest number recorded. Our bibliometric analysis provides a comprehensive mapping of DENV research across multiple dimensions, including vector ecology, virology, and emerging therapies. The study delineates a complex network of immune response genes, including IFNA1, DDX58, IFNB1, STAT1, IRF3, and NFKB1, highlighting significant trends and emerging themes, particularly the impacts of climate change and new outbreaks on disease transmission. Our findings detail the progress and current status of key vaccine candidates, including the licensed Dengvaxia, newer vaccines such as Qdenga and TV003, and updated clinical trials. The study underscores significant advancements in antiviral therapies and vector control strategies for dengue, highlighting innovative drug candidates such as AT-752 and JNJ-1802, and the potential of drug repurposing with agents like Ribavirin, Remdesivir, and Lopinavir. Additionally, it discusses biological control methods, including the introduction of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes and gene-editing technologies.
Conclusion: This bibliometric study underscores the critical role of interdisciplinary collaboration in advancing DENV research, identifying key trends and areas needing further exploration, including host-virus dynamics, the development and application of antiviral drugs and vaccines, and the use of artificial intelligence. It advocates for strengthened partnerships across various disciplines to effectively tackle the challenges posed by DENV.
Keywords: Antiviral therapies; Bibliometric Analysis; Dengue Virus (DENV); Global Research Trends; Vaccine Development; Vector Control Strategies.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that has no competing interests.
Figures
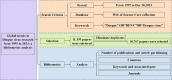


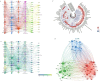
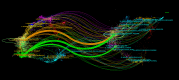
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

