EP300-mediated H3 acetylation elevates MTHFD2 expression to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced tubular epithelial cells
- PMID: 39230047
- PMCID: PMC11376309
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2369342
EP300-mediated H3 acetylation elevates MTHFD2 expression to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide-induced tubular epithelial cells
Abstract
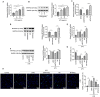
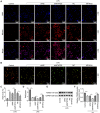
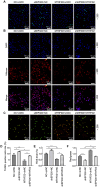
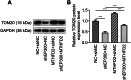
Sepsis represents an organ dysfunction resulting from the host's maladjusted response to infection, and can give rise to acute kidney injury (AKI), which significantly increase the morbidity and mortality of septic patients. This study strived for identifying a novel therapeutic strategy for patients with sepsis-induced AKI (SI-AKI). Rat tubular epithelial NRK-52E cells were subjected to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) exposure for induction of in-vitro SI-AKI. The expressions of E1A binding protein p300 (EP300) and methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2 (MTHFD2) in NRK-52E cells were assessed by western blot and qRT-PCR, and their interaction was explored by chromatin immunoprecipitation performed with antibody for H3K27 acetylation (H3K27ac). The effect of them on SI-AKI-associated mitochondrial dysfunction of tubular epithelial cells was investigated using transfection, MTT assay, TUNEL staining, 2',7'-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate probe assay, Mitosox assay, and JC-1 staining. MTHFD2 and EP300 were upregulated by LPS exposure in NRK-52E cells. LPS increased the acetylation of H3 histone in the MTHFD2 promoter region, and EP300 suppressed the effect of LPS. EP300 ablation inhibited the expression of MTHFD2. MTHFD2 overexpression antagonized LPS-induced viability reduction, apoptosis promotion, reactive oxygen species overproduction, and mitochondrial membrane potential collapse of NRK-52E cells. By contrast, MTHFD2 knockdown and EP300 ablation brought about opposite consequences. Furthermore, MTHFD2 overexpress and EP300 ablation counteracted each other's effect in LPS-exposed NRK-52E cells. EP300-mediated H3 acetylation elevates MTHFD2 expression to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction of tubular epithelial cells in SI-AKI.
Keywords: E1A binding protein p300; methylenetetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase 2; mitochondrial dysfunction; sepsis-induced acute kidney injury; tubular epithelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
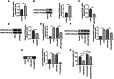
References
-
- Huang SJ, Ai T, Hu H, et al. Immunotherapy for sepsis induced by infections: clinical evidence and potential targets. Discov Med. 2022;34(172):83–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
