Diagnostic accuracy of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39230596
- PMCID: PMC11374877
- DOI: 10.1007/s10238-024-01478-x
Diagnostic accuracy of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
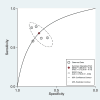
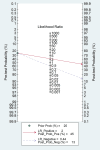
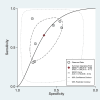
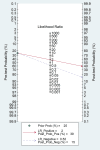
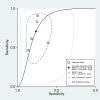
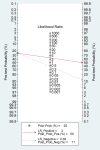
Existing challenges with the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and active disease, mainly by non-rheumatologists, have prompted the search for novel biomarkers. Elevations in indices derived from blood cell counts, e.g., the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), have been reported in RA patients. However, their diagnostic accuracy has not been comprehensively assessed. Therefore, we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies reporting the sensitivity and specificity of the NLR and PLR, obtained by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis, for the presence of RA and active disease. We searched electronic databases from inception to 15 March 2024 and assessed the risk of bias using the JBI Critical Appraisal Checklist (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42024533546). In 15 studies, the NLR exhibited acceptable accuracy for the presence of RA (area under the curve, AUC = 0.76, 95% CI 0.72 to 0.80) and active disease (AUC = 0.70, 95% CI 0.66 to 0.74). The PLR exhibited good accuracy for the presence of RA (AUC = 0.80, 95% CI 0.76 to 0.83). There were insufficient studies to assess the accuracy of the PLR for the presence of active disease. Our systematic review and meta-analysis suggests that the NLR and the PLR are promising biomarkers of RA (NLR and PLR) and active disease (NLR). Further research is required to investigate whether the NLR and PLR can significantly enhance the capacity to diagnose RA and active disease in clinical practice.
Keywords: Active disease; Diagnostic accuracy; Lymphocyte ratio; Neutrophil; Platelet; Rheumatoid arthritis; To.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

