Halide Perovskite Induces Halogen/Hydrogen Atom Transfer (XAT/HAT) for Allylic C-H Amination
- PMID: 39231037
- PMCID: PMC11701359
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202413012
Halide Perovskite Induces Halogen/Hydrogen Atom Transfer (XAT/HAT) for Allylic C-H Amination
Abstract
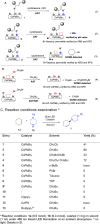
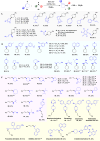
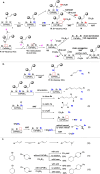
Allylic C-H amination has emerged as a powerful tool to construct allylamines, common motifs in molecular therapeutics. Such reaction implies an oxidative path for C-H activation but furnishes reductive amines, inferring mild oxidants' inactivity for C-H oxidation but strong oxidants' detriment to products. Herein we report a heterogeneous catalytic approach that manipulates halogen-vacancies of perovskite photocatalyst and exploits halogenated-solvents (i.e. CH2Cl2, CH2Br2) as mild oxidants for selective C-H allyl amination with 19,376 turnovers. CsPbBr3 nanocrystals induce cooperative hydrogen-atom-transfer (HAT, C-H oxidation, and halogen-vacancy CsPbBr3-x formation) and halogen-atom-transfer (XAT, CsPbBr3-x-induced solvent reduction) under a radical chain mechanism. Terminal/internal olefins are amenable to forge aromatic/aliphatic, cyclic/acyclic, secondary/tertiary allylamines (70 examples), including drugs or their derivatives.
Keywords: C−H amination; Halide perovskite; Halogen atom transfer; Hydrogen atom transfer; Photocatalyst.
© 2024 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
A provisional patent application is filing during the manuscript preparation.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

