Less experienced observers assess piglet castration-induced acute pain differently than experienced observers: A pilot study
- PMID: 39231102
- PMCID: PMC11373819
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0309684
Less experienced observers assess piglet castration-induced acute pain differently than experienced observers: A pilot study
Abstract
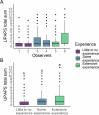
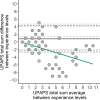
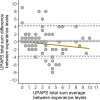
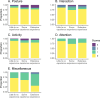
Behavioral pain scales have been helpful for standardized swine pain assessment. However, it is still unknown if observers' experience influences the scale score. We conducted a pilot study to investigate how three different levels of swine experience influenced how observers scored castration pain in piglets using Unesp-Botucatu Pig Composite Acute Pain Scale (UPAPS). We used a database from UPAPS scores from pigs undergoing surgical castration in a previous study. Scores were attributed by six observers with Little to no experience (n = 2), Some experience (n = 2) and Extensive experience (n = 2). Reliability was estimated using the intraclass correlation coefficient, agreement was investigated by Bland-Altman analysis, predictive capacity was estimated using the area under the curve (AUC), and statistical differences were tested using a regression model. We found that intra-experience levels reliability were satisfactory (Little to no: 0.72, Some: 0.81, Extensive: 0.84), but inter-experience reliability was lower (0.42). Little to no experience observers had poor agreement with other observers, with a bias toward underscoring UPAPS (bias of 0.94 vs. Some, 1.17 vs. Extensive). Predictive capacity was similar between all observers (AUC, Little to no: 71.94%, Some: 76.10%, Extensive: 79.09%, p > 0.05). Regression model confirmed underscoring of Little to no experience observers (mean ± standard error; Little to no: 1.09 ± 0.14; Some: 2.02 ± 0.23; Extensive: 2.25 ± 0.22; p < 0.05). We concluded that minimal experience, as Some experience observers have in the swine industry, is sufficient for them to score UPAPS in a similar way than more experienced observers. The present pilot study supports the enhancement and implementation of UPAPS on farm and laboratory settings by minimally qualified observers, improving swine welfare in the short and long term.
Copyright: © 2024 Silva et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Validation of the Unesp-Botucatu pig composite acute pain scale (UPAPS) in piglets undergoing castration.PLoS One. 2023 Apr 13;18(4):e0284218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0284218. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37053294 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of assessment method (real-time versus video-recorded) on a validated pain-altered behavior scale used in castrated piglets.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 31;13(1):18680. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45869-8. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37907564 Free PMC article.
-
Proposing a short version of the Unesp-Botucatu pig acute pain scale using a novel application of machine learning technique.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 28;15(1):7161. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91551-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40021814 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement properties of pain scoring instruments in farm animals: A systematic review using the COSMIN checklist.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 20;18(1):e0280830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280830. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36662813 Free PMC article.
-
Proposed multidimensional pain outcome methodology to demonstrate analgesic drug efficacy and facilitate future drug approval for piglet castration.Anim Health Res Rev. 2021 Dec;22(2):163-176. doi: 10.1017/S1466252321000141. Epub 2021 Dec 3. Anim Health Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 34859764 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical validation of the Unesp-Botucatu acute pain scale in sheep undergoing orthopedic surgery.PLoS One. 2025 May 12;20(5):e0323132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0323132. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40354487 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Meat Market Review—Emerging trends and outlook 2022.
-
- Camerlink I, Ursinus WW. Tail postures and tail motion in pigs: A review. Applied Animal Behaviour Science. 2020. Sep 1;230:105079.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

