High-resolution stereolithography: Negative spaces enabled by control of fluid mechanics
- PMID: 39231205
- PMCID: PMC11406279
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2405382121
High-resolution stereolithography: Negative spaces enabled by control of fluid mechanics
Abstract
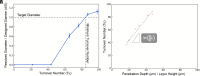
Stereolithography enables the fabrication of three-dimensional (3D) freeform structures via light-induced polymerization. However, the accumulation of ultraviolet dose within resin trapped in negative spaces, such as microfluidic channels or voids, can result in the unintended closing, referred to as overcuring, of these negative spaces. We report the use of injection continuous liquid interface production to continuously displace resin at risk of overcuring in negative spaces created in previous layers with fresh resin to mitigate the loss of Z-axis resolution. We demonstrate the ability to resolve 50-μm microchannels, breaking the historical relationship between resin properties and negative space resolution. With this approach, we fabricated proof-of-concept 3D free-form microfluidic devices with improved design freedom over device material selection and resulting properties.
Keywords: 3D-printing; microfluidics; negative-space; stereolithography; vat-polymerization.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:J.M.D. declares that he has an equity stake in Carbon Inc., a venture-backed start-up company that owns U.S. Patent 9,216,546, U.S. Patent 9,360,757, and other related patents. I.A.C., G.L., and J.M.D. declare that they are currently listed as inventors on a pending patent application for methods involving negative space preservation using iCLIP. The CLIP and iCLIP patents and patent applications are being licensed to a new vaccine and drug delivery company called PinPrint, which J.M.D. is a founder of and in which he holds an equity stake. M.A.S. advises 3D Architech Inc., a company specializing in vat photopolymerization-based metal 3D printing. The authors declare that they have no other competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Therriault D., White S. R., Lewis J. A., Chaotic mixing in three-dimensional microvascular networks fabricated by direct-write assembly. Nat. Mater. 2, 265–271 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Wu S.-Y., Yang C., Hsu W., Lin L., 3D-printed microelectronics for integrated circuitry and passive wireless sensors. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 1, 15013 (2015).
-
- Sun K., et al. , 3D printing of interdigitated Li-ion microbattery architectures. Adv. Mater. 25, 4539–4543 (2013). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

