ERRα and ERRγ coordinate expression of genes associated with Alzheimer's disease, inhibiting DKK1 to suppress tau phosphorylation
- PMID: 39231208
- PMCID: PMC11406303
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2406854121
ERRα and ERRγ coordinate expression of genes associated with Alzheimer's disease, inhibiting DKK1 to suppress tau phosphorylation
Abstract
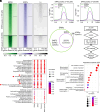
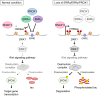
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a prevalent neurodegenerative disease characterized by cognitive decline and learning/memory impairment associated with neuronal cell loss. Estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα) and ERRγ, which are highly expressed in the brain, have emerged as potential AD regulators, with unelucidated underlying mechanisms. Here, we identified genome-wide binding sites for ERRα and ERRγ in human neuronal cells. They commonly target a subset of genes associated with neurodegenerative diseases, including AD. Notably, Dickkopf-1 (DKK1), a Wnt signaling pathway antagonist, was transcriptionally repressed by both ERRα and ERRγ in human neuronal cells and brain. ERRα and ERRγ repress RNA polymerase II (RNAP II) accessibility at the DKK1 promoter by modulating a specific active histone modification, histone H3 lysine acetylation (H3K9ac), with the potential contribution of their corepressor. This transcriptional repression maintains Wnt signaling activity, preventing tau phosphorylation and promoting a healthy neuronal state in the context of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; DKK1; PROX1; Wnt signaling pathway; estrogen-related receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests statement:The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures




References
-
- Hardy J., Selkoe D. J., The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297, 353–356 (2002). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

