The emerging role of SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 (nsp1) in epigenetic regulation of host gene expression
- PMID: 39231808
- PMCID: PMC11418652
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuae023
The emerging role of SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 (nsp1) in epigenetic regulation of host gene expression
Abstract
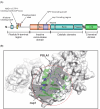
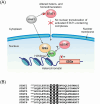
Infection with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) causes widespread changes in epigenetic modifications and chromatin architecture in the host cell. Recent evidence suggests that SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 (nsp1) plays an important role in driving these changes. Previously thought to be primarily involved in host translation shutoff and cellular mRNA degradation, nsp1 has now been shown to be a truly multifunctional protein that affects host gene expression at multiple levels. The functions of nsp1 are surprisingly diverse and include not only the downregulation of cellular mRNA translation and stability, but also the inhibition of mRNA export from the nucleus, the suppression of host immune signaling, and, most recently, the epigenetic regulation of host gene expression. In this review, we first summarize the current knowledge on SARS-CoV-2-induced changes in epigenetic modifications and chromatin structure. We then focus on the role of nsp1 in epigenetic reprogramming, with a particular emphasis on the silencing of immune-related genes. Finally, we discuss potential molecular mechanisms underlying the epigenetic functions of nsp1 based on evidence from SARS-CoV-2 interactome studies.
Keywords: DNA polymerase alpha; H3K9me2; coronavirus; epigenetic silencing; heterochromatin; nsp1.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenetic repression of antiviral genes by SARS-CoV-2 NSP1.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 26;19(1):e0297262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297262. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38277395 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine 164 is critical for SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 inhibition of host gene expression.J Gen Virol. 2021 Jan;102(1):jgv001513. doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001513. Epub 2020 Nov 5. J Gen Virol. 2021. PMID: 33151142 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal domain of SARS-CoV-2 nsp1 plays key roles in suppression of cellular gene expression and preservation of viral gene expression.Cell Rep. 2021 Oct 19;37(3):109841. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109841. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34624207 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of Coronavirus Nsp1-Mediated Control of Host and Viral Gene Expression.Cells. 2021 Feb 2;10(2):300. doi: 10.3390/cells10020300. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33540583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus nonstructural protein 1: Common and distinct functions in the regulation of host and viral gene expression.Virus Res. 2015 Apr 16;202:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2014.11.019. Epub 2014 Nov 26. Virus Res. 2015. PMID: 25432065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evolution: Implications for Diagnosis, Treatment, Vaccine Effectiveness and Development.Vaccines (Basel). 2024 Dec 28;13(1):17. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13010017. Vaccines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39852796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmed S, Saini S, Arora S et al. Chromodomain protein Swi6-mediated role of DNA polymerase alpha in establishment of silencing in fission yeast. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:47814–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

