Is Chronic Ice Water Ingestion a Risk Factor for Gastric Cancer Development? An Evidence-Based Hypothesis Focusing on East Asian Populations
- PMID: 39231856
- PMCID: PMC11573998
- DOI: 10.1007/s40487-024-00299-y
Is Chronic Ice Water Ingestion a Risk Factor for Gastric Cancer Development? An Evidence-Based Hypothesis Focusing on East Asian Populations
Abstract
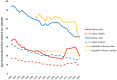
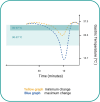
This article introduces a novel risk factor for gastric cancer (GC) by analyzing available epidemiological data from East Asian populations. A significantly higher age-standardized GC rate was observed in Japanese and Korean populations than in Chinese populations, despite nearly identical ethnicity, food habits, obesity rates, and alcohol consumption. Given the pivotal role of environmental factors in GC development, particularly for the intestinal type, a thorough evaluation of the lifestyles of these three populations was conducted to identify commonalities and disparities. It was observed that Japanese and Korean individuals prefer consuming ice water, while Chinese individuals tend to drink warm water, potentially influenced by traditional Chinese medicine disciplines. Considering the key features of GC development, a literature review was conducted to investigate the mechanisms through which the consumption of ice water might contribute to GC initiation and progression. Mechanistically, exposing gastric cells to hypothermia can increase the risk of carcinogenesis through multiple pathways. This includes the promotion of Helicobacter pylori colonization, prolonged gastric inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction in gastric cells. Furthermore, drinking ice water can enhance the survival, proliferation, and invasion of GC cells by releasing cold shock proteins, increasing gastric acid secretion, and delaying gastric emptying. Additionally, hypothermia can boost the immune evasion of cancer cells by weakening the antitumor immune system and activating different components of the tumor microenvironment. This paper also explores the association between exposure of GC cells to hypothermia and current insights into cancer hallmarks. These findings may partially elucidate the higher incidence of GC in Japanese and Korean populations and provide a clue for future experimental studies.Graphical abstract available for this article.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Ice water; Immune system; Mitochondria; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of alcohol consumption, ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism, and Helicobacter pylori infection on the gastric cancer risk in a Korean population.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6630-6641. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14250. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036260 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprevention of gastric cancer development after Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in an East Asian population: Meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Apr 21;26(15):1820-1840. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i15.1820. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32351296 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on molecular mechanism of pyroptosis caused by Helicobacter pylori in gastric cancer.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Feb 15;86(4):2016-2022. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001802. eCollection 2024 Apr. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38576917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary glycation compounds - implications for human health.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024 Sep;54(8):485-617. doi: 10.1080/10408444.2024.2362985. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39150724
-
GADD45B regulates the carcinogenesis process of chronic atrophic gastritis and the metabolic pathways of gastric cancer.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Aug 7;14:1224832. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1224832. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37608794 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TSGA10 as a Model of a Thermal Metabolic Regulator: Implications for Cancer Biology.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 23;17(11):1756. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111756. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507237 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azadeh P, Gholizadeh Pasha S, Yaghobi Joybari A, Abiar Z, Alahyari S, Taghizadeh-Hesary F. Survival benefit of induction chemotherapy with paclitaxel and carboplatin followed by chemoradiation versus postoperative treatment in locally advanced gastric cancer: a retrospective cohort study. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2023;55:457–66. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–49. - PubMed
-
- Plummer M, Franceschi S, Vignat J, Forman D, Martel C. Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(2):487–90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

