Natural killer (NK) cells-related gene signature reveals the immune environment heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma based on single cell analysis
- PMID: 39231877
- PMCID: PMC11374944
- DOI: 10.1007/s12672-024-01287-4
Natural killer (NK) cells-related gene signature reveals the immune environment heterogeneity in hepatocellular carcinoma based on single cell analysis
Abstract
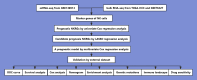
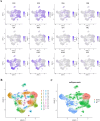
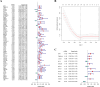
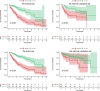
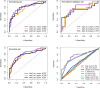
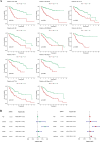
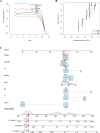
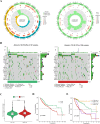
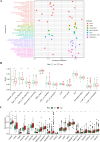
The early diagnosis of liver cancer is crucial for the treatment and depends on the coordinated use of several test procedures. Early diagnosis is crucial for precision therapy in the treatment of the hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Therefore, in this study, the NK cell-related gene prediction model was used to provide the basis for precision therapy at the gene level and a novel basis for the treatment of patients with liver cancer. Natural killer (NK) cells have innate abilities to recognize and destroy tumor cells and thus play a crucial function as the "innate counterpart" of cytotoxic T cells. The natural killer (NK) cells is well recognized as a prospective approach for tumor immunotherapy in treating patients with HCC. In this research, we used publicly available databases to collect bioinformatics data of scRNA-seq and RNA-seq from HCC patients. To determine the NK cell-related genes (NKRGs)-based risk profile for HCC, we isolated T and natural killer (NK) cells and subjected them to analysis. Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection plots were created to show the degree of expression of each marker gene and the distribution of distinct clusters. The connection between the immunotherapy response and the NKRGs-based signature was further analyzed, and the NKRGs-based signature was established. Eventually, a nomogram was developed using the model and clinical features to precisely predict the likelihood of survival. The prognosis of HCC can be accurately predicted using the NKRGs-based prognostic signature, and thorough characterization of the NKRGs signature of HCC may help to interpret the response of HCC to immunotherapy and propose a novel tumor treatment perspective.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma; Immunotherapy; Machine learning; Natural killer cells; Precision therapy; Prognostic signature.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
