Feature-Based vs. Deep-Learning Fusion Methods for the In Vivo Detection of Radiation Dermatitis Using Optical Coherence Tomography, a Feasibility Study
- PMID: 39231883
- PMCID: PMC11950469
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01241-4
Feature-Based vs. Deep-Learning Fusion Methods for the In Vivo Detection of Radiation Dermatitis Using Optical Coherence Tomography, a Feasibility Study
Abstract
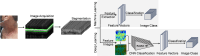
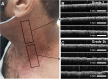
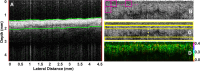
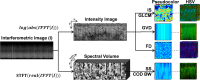
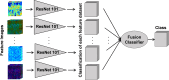
Acute radiation dermatitis (ARD) is a common and distressing issue for cancer patients undergoing radiation therapy, leading to significant morbidity. Despite available treatments, ARD remains a distressing issue, necessitating further research to improve prevention and management strategies. Moreover, the lack of biomarkers for early quantitative assessment of ARD impedes progress in this area. This study aims to investigate the detection of ARD using intensity-based and novel features of Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) images, combined with machine learning. Imaging sessions were conducted twice weekly on twenty-two patients at six neck locations throughout their radiation treatment, with ARD severity graded by an expert oncologist. We compared a traditional feature-based machine learning technique with a deep learning late-fusion approach to classify normal skin vs. ARD using a dataset of 1487 images. The dataset analysis demonstrates that the deep learning approach outperformed traditional machine learning, achieving an accuracy of 88%. These findings offer a promising foundation for future research aimed at developing a quantitative assessment tool to enhance the management of ARD.
Keywords: Acute radiation dermatitis; Classification; Deep learning; Feature extraction; Machine learning; Optical Coherence Tomography.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: This study was performed in accordance with the legislation of the Republic of Cyprus. Approval was granted by the Bioethics Committee of Cyprus (Jan 11 2021 / No: ΕΕΒΚ/ΕΠ/2020/61). Consent to Participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. The authors affirm that human research participants provided informed consent for publication of the image in Fig. 1A, Conflict of Interest: The authors have no relevant financial interests in this article and no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Oguchi M, Komura J, Ofuji S. (1978) Ultrastructural studies of epidermis in acute radiation dermatitis. Arch Dermatol Res.; 262(1): 73–81. 1. 10.1007/BF00455575 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
