L3MBTL1, a polycomb protein, promotes Osimertinib acquired resistance through epigenetic regulation of DNA damage response in lung adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 39231972
- PMCID: PMC11374981
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06796-2
L3MBTL1, a polycomb protein, promotes Osimertinib acquired resistance through epigenetic regulation of DNA damage response in lung adenocarcinoma
Abstract
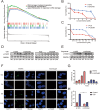
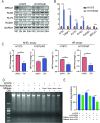
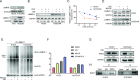
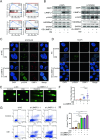
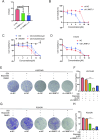
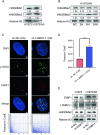
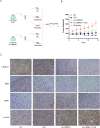
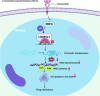
Osimertinib is a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) approved for patients with EGFR T790M resistance mutations as first- or second-line treatment of EGFR-positive patients. Resistance to Osimertinib will inevitably develop, and the underlying mechanisms are largely unknown. In this study, we discovered that acquired resistance to Osimertinib is associated with abnormal DNA damage response (DDR) in lung adenocarcinoma cells. We discovered that the polycomb protein Lethal(3) Malignant Brain Tumor-Like Protein 1 (L3MBTL1) regulates chromatin structure, thereby contributing to DDR and Osimertinib resistance. EGFR oncogene inhibition reduced L3MBTL1 ubiquitination while stabilizing its expression in Osimertinib-resistant cells. L3MBTL1 reduction and treatment with Osimertinib significantly inhibited DDR and proliferation of Osimertinib-resistant lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. L3MBTL1 binds throughout the genome and plays an important role in EGFR-TKI resistance. It also competes with 53BP1 for H4K20Me2 and inhibits the development of drug resistance in Osimertinib-resistant lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Our findings suggest that L3MBTL1 inhibition is a novel approach to overcoming EGFR-TKI-acquired resistance.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82072595 and 61973232/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82172569/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- TJYXZDXK-061B,TJWJ2022XK00/Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (Tianjin Health and Family Planning Commission)
- 5ZC20179/Tianjin Municipal Health Bureau (Tianjin Health and Family Planning Commission)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

