APIS: a paired CT-MRI dataset for ischemic stroke segmentation - methods and challenges
- PMID: 39232010
- PMCID: PMC11374904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-71273-x
APIS: a paired CT-MRI dataset for ischemic stroke segmentation - methods and challenges
Abstract
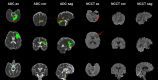
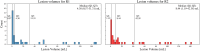
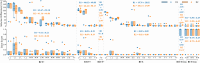
Stroke, the second leading cause of mortality globally, predominantly results from ischemic conditions. Immediate attention and diagnosis, related to the characterization of brain lesions, play a crucial role in patient prognosis. Standard stroke protocols include an initial evaluation from a non-contrast CT to discriminate between hemorrhage and ischemia. However, non-contrast CTs lack sensitivity in detecting subtle ischemic changes in this phase. Alternatively, diffusion-weighted MRI studies provide enhanced capabilities, yet are constrained by limited availability and higher costs. Hence, we idealize new approaches that integrate ADC stroke lesion findings into CT, to enhance the analysis and accelerate stroke patient management. This study details a public challenge where scientists applied top computational strategies to delineate stroke lesions on CT scans, utilizing paired ADC information. Also, it constitutes the first effort to build a paired dataset with NCCT and ADC studies of acute ischemic stroke patients. Submitted algorithms were validated with respect to the references of two expert radiologists. The best achieved Dice score was 0.2 over a test study with 36 patient studies. Despite all the teams employing specialized deep learning tools, results reveal limitations of computational approaches to support the segmentation of small lesions with heterogeneous density.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Deep learning; Image segmentation; Ischemic stroke; Paired dataset.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Big Data Approaches to Phenotyping Acute Ischemic Stroke Using Automated Lesion Segmentation of Multi-Center Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data.Stroke. 2019 Jul;50(7):1734-1741. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025373. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Stroke. 2019. PMID: 31177973 Free PMC article.
-
Robust Ensemble of Two Different Multimodal Approaches to Segment 3D Ischemic Stroke Segmentation Using Brain Tumor Representation Among Multiple Center Datasets.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Oct;37(5):2375-2389. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01099-6. Epub 2024 May 1. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38693333 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning models for ischemic stroke lesion segmentation in medical images: A survey.Comput Biol Med. 2024 Jun;175:108509. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108509. Epub 2024 Apr 25. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38677171 Review.
-
Segmentation of infarct lesions and prognosis prediction for acute ischemic stroke using non-contrast CT scans.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025 Jan;258:108488. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2024.108488. Epub 2024 Nov 5. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39531808
-
Automated CT Perfusion Imaging to Aid in the Selection of Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke for Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020 Nov 2;20(13):1-87. eCollection 2020. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2020. PMID: 33240454 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Core-Penumbra Hyperacute Ischemic Stroke Dataset.Sci Data. 2025 Apr 29;12(1):707. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05000-0. Sci Data. 2025. PMID: 40301380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Powers, W. J. et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke50, e344–e418 (2019). 10.1161/STR.0000000000000211 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

