An aberrant immune-epithelial progenitor niche drives viral lung sequelae
- PMID: 39232171
- PMCID: PMC12456998
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-024-07926-8
An aberrant immune-epithelial progenitor niche drives viral lung sequelae
Abstract
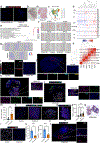
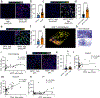
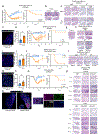
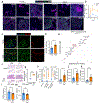
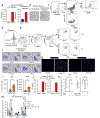
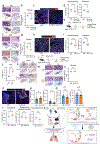
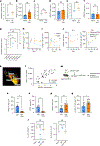
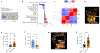
The long-term physiological consequences of respiratory viral infections, particularly in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic-termed post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 (PASC)-are rapidly evolving into a major public health concern1-3. While the cellular and molecular aetiologies of these sequelae are poorly defined, increasing evidence implicates abnormal immune responses3-6 and/or impaired organ recovery7-9 after infection. However, the precise mechanisms that link these processes in the context of PASC remain unclear. Here, with insights from three cohorts of patients with respiratory PASC, we established a mouse model of post-viral lung disease and identified an aberrant immune-epithelial progenitor niche unique to fibroproliferation in respiratory PASC. Using spatial transcriptomics and imaging, we found a central role for lung-resident CD8+ T cell-macrophage interactions in impairing alveolar regeneration and driving fibrotic sequelae after acute viral pneumonia. Specifically, IFNγ and TNF derived from CD8+ T cells stimulated local macrophages to chronically release IL-1β, resulting in the long-term maintenance of dysplastic epithelial progenitors and lung fibrosis. Notably, therapeutic neutralization of IFNγ + TNF or IL-1β markedly improved alveolar regeneration and pulmonary function. In contrast to other approaches, which require early intervention10, we highlight therapeutic strategies to rescue fibrotic disease after the resolution of acute disease, addressing a current unmet need in the clinical management of PASC and post-viral disease.
© 2024. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Update of
-
Proximal immune-epithelial progenitor interactions drive chronic tissue sequelae post COVID-19.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 28:rs.3.rs-3587418. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3587418/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Nature. 2024 Oct;634(8035):961-969. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07926-8. PMID: 38077031 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 AG090337/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL164049/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007496/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI176171/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132177/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM133712/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI147394/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL170961/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL167202/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI112844/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL159953/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132287/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI154598/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI178669/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL155759/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 HL150803/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- F31 HL170746/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG047156/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG069264/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

