Urinary CXCL-10, a prognostic biomarker for kidney graft injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39232662
- PMCID: PMC11375915
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-024-03728-2
Urinary CXCL-10, a prognostic biomarker for kidney graft injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
The challenges of long-term graft survival and the side effects of current immunosuppressive therapies in kidney transplantation highlight the need for improved drugs with fewer adverse effects. Biomarkers play a crucial role in quickly detecting post-transplant complications, with new biomarkers showing promise for ongoing monitoring of disease and potentially reducing the need for unnecessary invasive biopsies. The chemokines such as C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10), are particularly promising protein biomarkers for acute renal rejection, with urine samples being a desirable source for biomarkers. The aim of this review is to analyze the literature on the potential role of urinary CXCL10 protein in predicting kidney graft injuries. The results of this study demonstrate that evaluating urinary CXCL10 levels is more successful in identifying post-transplant injuries compared to assessing the CXCL10/Cr ratio.
Keywords: Biomarker; CXCL10; Kidney graft; Meta-analysis; Urine.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
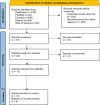
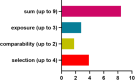
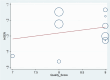


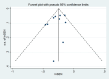
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

