Uncovering the key working mechanisms of a complex community-based obesity prevention programme in the Netherlands using ripple effects mapping
- PMID: 39232736
- PMCID: PMC11373344
- DOI: 10.1186/s12961-024-01182-y
Uncovering the key working mechanisms of a complex community-based obesity prevention programme in the Netherlands using ripple effects mapping
Abstract
Background: Much remains unknown about how complex community-based programmes can successfully achieve long-term impact. More insight is needed to understand the key mechanisms through which these programmes work. Therefore, we conducted an in-depth study in five communities that implemented the Healthy Youth, Healthy Future (JOGG) approach, a Dutch community-based obesity prevention programme. We aimed to identify perceived outcomes and long-term impacts among local stakeholders and explore potential causal pathways and working mechanisms.
Methods: We used ripple effects mapping (REM), a qualitative participatory method to map outcomes and identify causal pathways, in five communities. We involved 26 stakeholders, professionals and policy-makers affiliated with the local JOGG approach, spread over eight REM sessions and conducted individual interviews with 24 additional stakeholders. To uncover working mechanisms, we compared outcomes and causal pathways across communities.
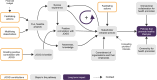
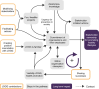
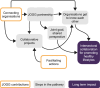
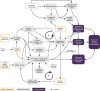
Results: Over 5-9 years of implementation, participants perceived that JOGG had improved ownership of local stakeholders, health policies, intersectoral collaboration and social norms towards promoting healthy lifestyles. Causal pathways comprised small initial outcomes that created the preconditions to enable the achievement of long-term impact. Although exact JOGG actions varied widely between communities, we identified five common working mechanisms through which the JOGG approach contributed to causal pathways: (1) creating a positive connotation with JOGG, (2) mobilizing stakeholders to participate in the JOGG approach, (3) facilitating projects to promote knowledge and awareness among stakeholders while creating successful experiences with promoting healthy lifestyles, (4) connecting stakeholders, thereby stimulating intersectoral collaboration and (5) sharing stakeholder successes that promote healthy lifestyles, which gradually created a social norm of participation.
Conclusions: The JOGG approach seems to work through activating initial stakeholder participation and bolstering the process towards ownership, policy change, and intersectoral collaboration to promote healthy lifestyles. Key working mechanisms can inform further development of JOGG as well as other complex community-based prevention programmes.
Keywords: Child; Community based; Complexity; Health promotion; Healthy lifestyle; Implementation; Intersectoral; Mechanisms; Obesity; Prevention; Stakeholders.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- OECD. The heavy burden of obesity. Paris: OECD Health Policy Studies, OECD Publishing; 2019.
-
- World Health Organization. Report on the fifth round of data collection, 2018–2020: WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI). Copenhagen; 2022. https://www.who.int/europe/publications/i/item/WHO-EURO-2022-6594-46360-....
-
- Moradi M, Mozaffari H, Askari M, Azadbakht L. Association between overweight/obesity with depression, anxiety, low self-esteem, and body dissatisfaction in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2020. 10.1080/10408398.2020.1823813. 10.1080/10408398.2020.1823813 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

