RBM8A, a new target of TEAD4, promotes breast cancer progression by regulating IGF1R and IRS-2
- PMID: 39232805
- PMCID: PMC11373126
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-024-05639-0
RBM8A, a new target of TEAD4, promotes breast cancer progression by regulating IGF1R and IRS-2
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is the most common malignant tumor in women worldwide, and further elucidation of the molecular mechanisms involved in BC pathogenesis is essential to improve the prognosis of BC patients. RNA Binding Motif Protein 8 A (RBM8A), with high affinity to a myriad of RNA transcripts, has been shown to play a crucial role in genesis and progression of multiple cancers. We attempted to explore its functional significance and molecular mechanisms in BC.
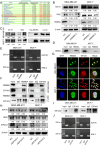
Methods: Bioinformatics analysis was performed on publicly available BC datasets. qRT-PCR was used to determine the expression of RBM8A in BC tissues. MTT assay, clone formation assay and flow cytometry were employed to examine BC cell proliferation and apoptosis in vitro. RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RIP-seq were used to investigate the binding of RBM8A/EIF4A3 to the mRNA of IGF1R/IRS-2. RBM8A and EIF4A3 interactions were determined by co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) and immunofluorescence. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (Ch-IP) and dual-luciferase reporter assay were carried out to investigate the transcriptional regulation of RBM8A by TEAD4. Xenograft model was used to explore the effects of RBM8A and TEAD4 on BC cell growth in vivo.
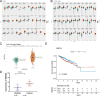
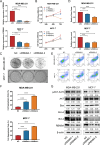
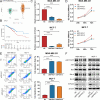
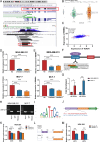
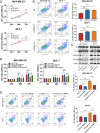
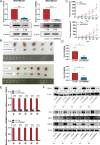
Results: In this study, we showed that RBM8A is abnormally highly expressed in BC and knockdown of RBM8A inhibits BC cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in vitro. EIF4A3, which phenocopy RBM8A in BC, forms a complex with RBM8A in BC. Moreover, EIF4A3 and RBM8A complex regulate the expression of IGF1R and IRS-2 to activate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby promoting BC progression. In addition, we identified TEAD4 as a transcriptional activator of RBM8A by Ch-IP, dual luciferase reporter gene and a series of functional rescue assays. Furthermore, we demonstrated the in vivo pro-carcinogenic effects of TEAD4 and RBM8A by xenograft tumor experiments in nude mice.
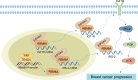
Conclusion: Collectively, these findings suggest that TEAD4 novel transcriptional target RBM8A interacts with EIF4A3 to increase IGF1R and IRS-2 expression and activate PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, thereby further promoting the malignant phenotype of BC cells.
Keywords: Breast cancer; EIF4A3; PI3K/AKT; RBM8A; TEAD4.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

